Today we are excited to announce the release of over twenty new BigQuery and BigQuery ML (BQML) operators for Vertex AI Pipelines, that help make it easier to operationalize BigQuery and BQML jobs in a Vertex AI Pipeline. The first five BigQuery and BQML pipeline components were released earlier this year. These twenty-one new, first-party, Google Cloud-supported components help data scientists, data engineers, and other users incorporate all of Google Cloud’s BQML capabilities including forecasting, explainable AI, and MLOps.
The seamless integration between BQML and Vertex AI helps automate and monitor the entire model life cycle of BQML models from training to serving. Developers, especially ML engineers, no longer have to write bespoke code in order to include BQML workflows in their ML pipelines, they can now simply include these new BQML components in their pipelines natively, making it easier and faster to deploy end-to-end ML lifecycle pipelines.
From our partners:
In addition, using these components as part of a Vertex AI Pipelines provides data and model governance. Any time a pipeline is executed, Vertex AI Pipelines tracks and manages any artifacts produced automatically.
For BigQuery, the following components are available:
| BigQuery | ||
|---|---|---|
| Category | Component | Description |
| Query | BigqueryQueryJobOp | Allows users to submit an arbitrary BQ query which will either be written to a temporary or permanent table. Launches a BigQuery query job and waits for it to finish.
|
For BigQuery ML (BQML), the following components are now available:
| BigQuery ML | ||
|---|---|---|
| Category | Component | Description |
| Core | BigqueryCreateModelJobOp | Allow users to submit a DDL statement to create a BigQuery ML model. |
| BigqueryEvaluateModelJobOp | Allows users to evaluate a BigQuery ML model. | |
| BigqueryPredictModelJobOp | Allows users to make predictions using a BigQuery ML model. | |
| BigqueryExportModelJobOp | Allows users to export a BigQuery ML model to a Google Cloud Storage bucket | |
| New Components | ||
|
Forecasting |
BigqueryForecastModelJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.FORECAST job and lets you forecast an ARIMA_PLUS or ARIMA model. |
| BigqueryExplainForecastModelJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST job and let you forecast an ARIMA_PLUS or ARIMA model | |
| BigqueryMLArimaEvaluateJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.ARIMA_EVALUATE job and waits for it to finish. | |
| Anomaly Detection |
BigqueryDetectAnomaliesModelJobOp | Launches a BigQuery detect anomaly model job and waits for it to finish. |
| Model Evaluation | BigqueryMLConfusionMatrixJobOp | Launches a BigQuery confusion matrix job and waits for it to finish. |
| BigqueryMLCentroidsJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.CENTROIDS job and waits for it to finish | |
| BigqueryMLTrainingInfoJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ml training info fetching job and waits for it to finish. | |
| BigqueryMLTrialInfoJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ml trial info job and waits for it to finish. | |
| BigqueryMLRocCurveJobOp | Launches a BigQuery roc curve job and waits for it to finish. | |
|
Explainable AI |
BigqueryMLGlobalExplainJobOp | Launches a BigQuery global explain fetching job and waits for it to finish. |
| BigqueryMLFeatureInfoJobOp | Launches a BigQuery feature info job and waits for it to finish. | |
| BigqueryMLFeatureImportanceJobOp | Launches a BigQuery feature importance fetch job and waits for it to finish. | |
| Model Weights | BigqueryMLWeightsJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ml weights job and waits for it to finish. |
| BigqueryMLAdvancedWeightsJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ml advanced weights job and waits for it to finish. | |
| BigqueryMLPrincipalComponentsJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.PRINCIPAL_COMPONENTS job and waits for it to finish. | |
| BigqueryMLPrincipalComponentInfoJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.principal_component_info job and waits for it to finish. | |
| BigqueryMLArimaCoefficientsJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.ARIMA_COEFFICIENTS job and lets you see the ARIMA coefficients. | |
| Model Inference | BigqueryMLReconstructionLossJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML reconstruction loss job and waits for it to finish. |
| BigqueryExplainPredictModelJobOp | Launches a BigQuery explain predict model job and waits for it to finish | |
| BigqueryMLRecommendJobOp | Launches a BigQuery ML.Recommend job and waits for it to finish. | |
| Other | BigqueryDropModelJobOp | Launches a BigQuery drop model job and waits for it to finish. |
Now that you have a broad overview of all pipeline operators for BQML available, let’s see how to use forecasting ones in the end-to-end example of building demand forecast predictions. You will find the code in the Vertex AI samples repo on Github.
Example of a demand forecast predictions pipeline in BigQuery ML
In this section, we’ll show an end-to-end example of using BigQuery and BQML components in a Vertex AI Pipeline for demand forecasting. The pipeline is based on the solving for food waste with data analytics blog post. In this scenario, a fictitious grocer, FastFresh, specialized in selling fresh food distribution, wants to minimize food waste and optimize stock levels across all stores. Due to the frequency of inventory updates (by minute of every single item), they want to train a demand forecasting model on an hourly basis. With 24 training jobs per day, they want to automate model training using an ML pipeline using pipeline operators for BQML ARIMA_PLUS, the forecasting model type in BQML.
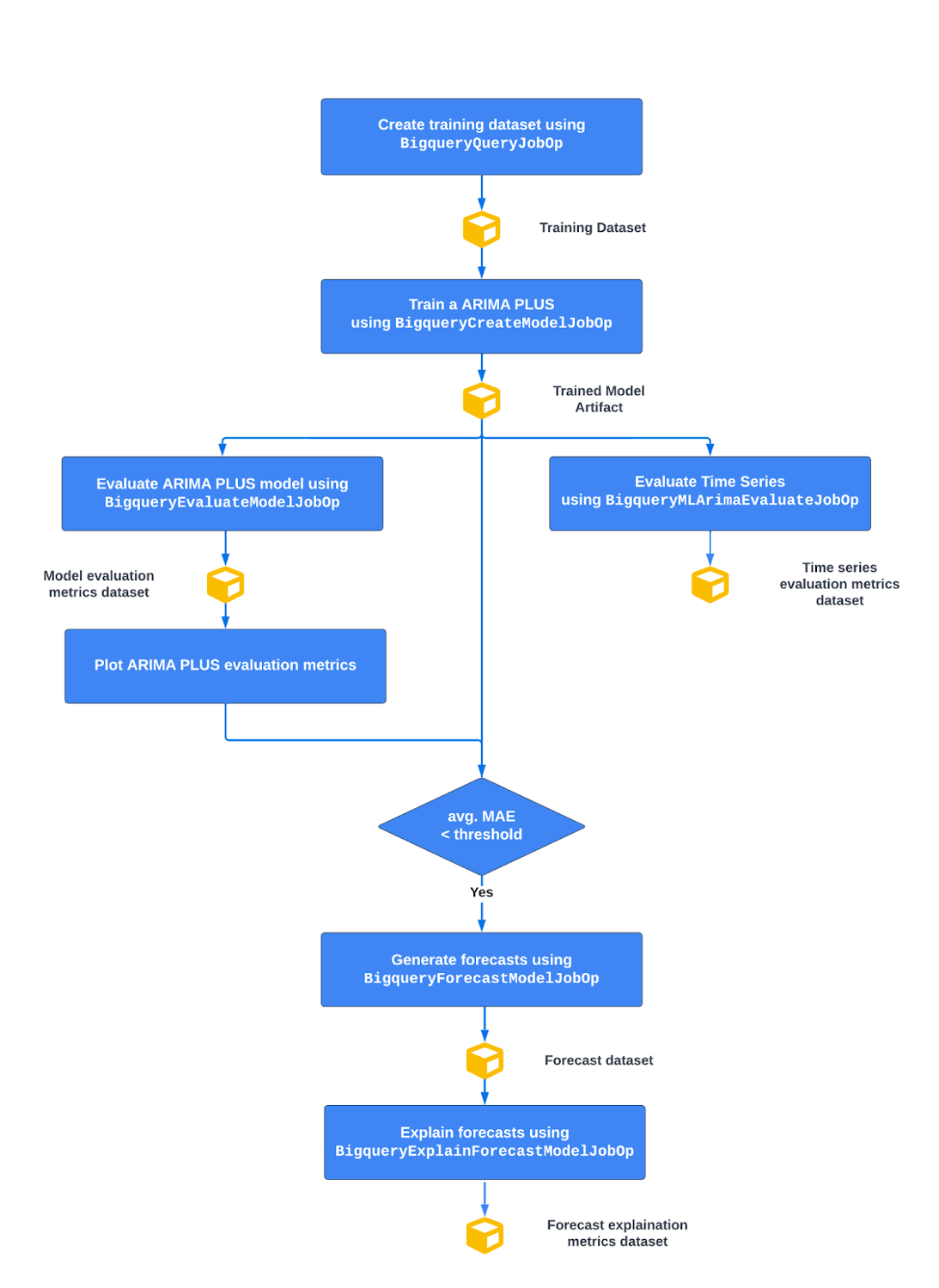
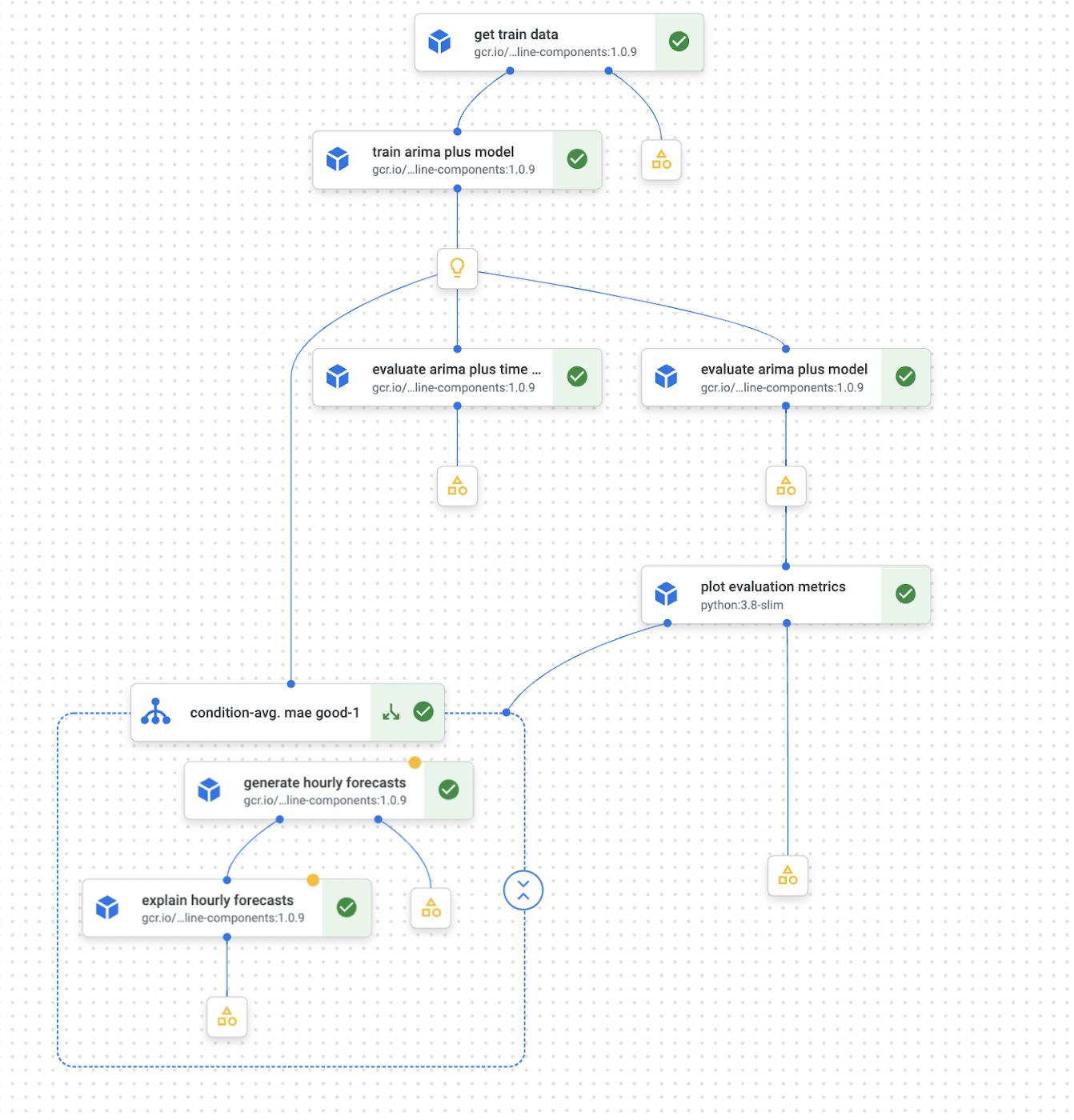
Below you can see a high level picture of the pipeline flow
From top to bottom:
- Create the training dataset in BigQuery
- Train a BigQuery ML ARIMA_PLUS model
- Evaluate ARIMA_PLUS time series and model metrics
Then, if the average mean absolute error (MAE), which measures the mean of the absolute value of the difference between the forecasted value and the actual value, is less than a certain threshold:
- Generate time series forecasts based on a trained time series ARIMA_PLUS model
- Generate separate time series components of both the training and the forecasting data to explain predictions
Let’s dive into the pipeline operators for BQML ARIMA_PLUS.
Training a demand forecasting model
Once you have the training data (as a table), you are ready to build a demand forecasting model with the ARIMA_PLUS algorithm. You can automate this BQML model creation operation within a Vertex AI Pipeline using the BigqueryCreateModelJobOp. As we discussed in the previous article, this component allows you to pass the BQML training query to submit a model training of an ARIMA_PLUS model on BigQuery. The component returns a google.BQMLModel which will be recorded in the Vertex ML Metadata so that you can keep track of the lineage of all artifacts. Below you find the model training operator where the set_display_name attribute allows you to name the component during the execution. And the after attribute allows you to control the sequential order of the pipeline step.
bq_arima_model_op = BigqueryCreateModelJobOp(query=f"""-- create model tableCREATE OR REPLACE MODEL `{project}.{bq_dataset}.{bq_model_table}`OPTIONS(MODEL_TYPE = \'ARIMA_PLUS\',TIME_SERIES_TIMESTAMP_COL = \'hourly_timestamp\',TIME_SERIES_DATA_COL = \'total_sold\',TIME_SERIES_ID_COL = [\'product_name\'],MODEL_REGISTRY = \'vertex_ai\',VERTEX_AI_MODEL_ID = \'order_demand_forecasting\',VERTEX_AI_MODEL_VERSION_ALIASES = [\'staging\']) ASSELECThourly_timestamp,product_name,total_soldFROM `{project}.{bq_dataset}.{bq_training_table}`WHERE split='TRAIN';""",project=project,location=location,).set_display_name("train arima plus model").after(create_training_dataset_op)
Evaluating time series and model metrics
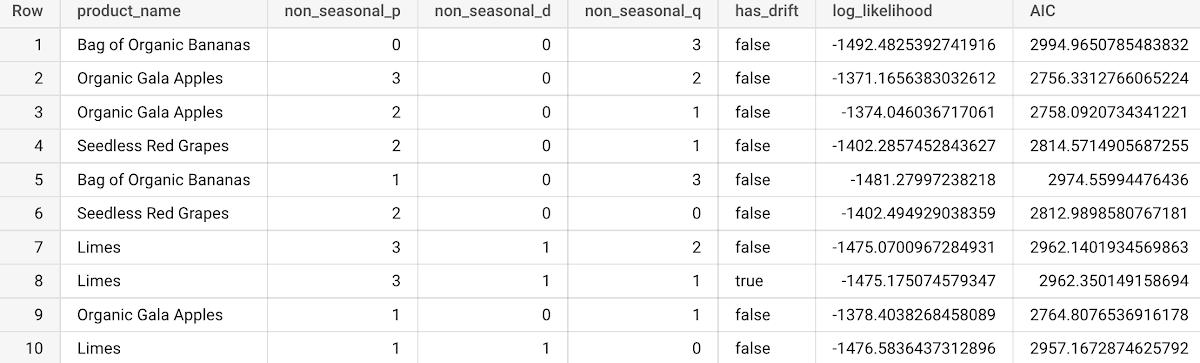
Once you train the ARIMA_PLUS model, you would need to evaluate the model before generating predictions. In BigQuery ML, you have ML.ARIMA_EVALUATE and ML.EVALUATE functions. The ML.ARIMA_EVALUATE function generates both statistical metrics such as log_likelihood, AIC, and variance and other time series information about seasonality, holiday effects, spikes-and-dips outliers, etc. for all the ARIMA models trained with the automatic hyperparameter tuning enabled by default (auto.ARIMA). The ML.EVALUATE retrieves forecasting accuracy metrics such as the mean absolute error (MAE) and the mean squared error (MSE). To integrate those evaluation functions in a Vertex AI pipeline you can now use the corresponding BigqueryMLArimaEvaluateJobOp and BigqueryEvaluateModelJobOp operators. In both cases they take google.BQMLModel as input and return Evaluation Metrics Artifact as output.
For the BigqueryMLArimaEvaluateJobOp, here is an example of it used in a pipeline component:
bq_arima_evaluate_time_series_op = BigqueryMLArimaEvaluateJobOp(project=project,location=location,model=bq_arima_model_op.outputs['model'],show_all_candidate_models='false',job_configuration_query=bq_evaluate_time_series_configuration).set_display_name("evaluate arima plus time series").after(bq_arima_model_op)
Below is the view of statistical metrics (the first five columns) resulting from BigqueryMLArimaEvaluateJobOp operators in a BigQuery table.
For the BigqueryEvaluateModelJobOp, below you have the corresponding pipeline component:
bq_arima_evaluate_model_op = BigqueryEvaluateModelJobOp(project=project,location=location,model=bq_arima_model_op.outputs['model'],query_statement=f"SELECT * FROM `<my_project_id>.<my_dataset_id>.<train_table_id>` WHERE split='TEST'",job_configuration_query=bq_evaluate_model_configuration).set_display_name("evaluate arima_plus model").after(bq_arima_model_op)
Where you have a query statement to select the test sample to generate evaluation forecast metrics.
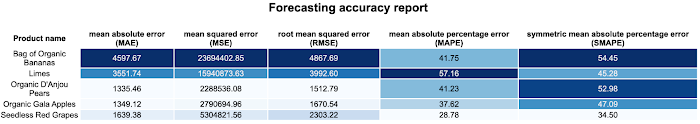
As Evaluation Metrics Artifacts in the Vertex ML metadata, you can consume those metrics afterwards for visualizations in the Vertex AI Pipelines UI using Kubeflow SDK visualization APIs. Indeed, Vertex AI allows you to render that HTML in an output page which is easily accessible from the Google Cloud console. Below is an example of a custom forecasting HTML report you can create.
Also you can use those values to implement conditional if-else logic using Kubeflow SDK condition in the pipeline graph. In this scenario, a model performance condition has been implemented using the average mean squared error in a way that if the trained model average mean squared error is below a certain threshold then the model can be consumed to generate forecast predictions.
Generate and explain demand forecasts
To generate forecasts in the next n hours, you can use the BigqueryForecastModelJobOp which launches a BigQuery forecast model job. The component consumes the google.BQMLModel as Input Artifact and allows you to set the number of time points to forecast (horizon) and the percentage of the future values that fall in the prediction interval (confidence_level). In the example below it has been decided to generate hourly forecasts with a confidence interval of 90%.
bq_arima_forecast_op = BigqueryForecastModelJobOp(project=project,location=location,model=bq_arima_model_op.outputs['model'],horizon=1,confidence_level=0.9,job_configuration_query=bq_forecast_configuration).set_display_name("generate hourly forecasts").after(get_evaluation_model_metrics_op
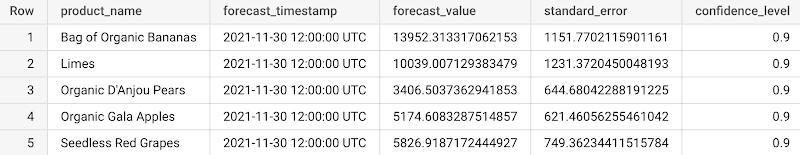
Then forecasts are materialized in a predefined destination table using the job_configuration_query parameter which will be tracked as google.BQTable in the Vertex ML Metadata. Below is an example of the forecast table you would get (only the five columns).
After you generate your forecasts, you can also explain them using the BigqueryExplainForecastModelJobOp which extends the capabilities of BigqueryForecastModelJobOp operator and allows to use the ML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST function which provides extra model explainability like trend, detected seasonality, and holiday effects.
bq_arima_explain_forecast_op = BigqueryExplainForecastModelJobOp(project=project,location=location,model=bq_arima_model_op.outputs['model'],horizon=1,confidence_level=0.9,job_configuration_query=bq_explain_forecast_configuration).set_display_name("explain hourly forecasts").after(bq_arima_forecast_op)
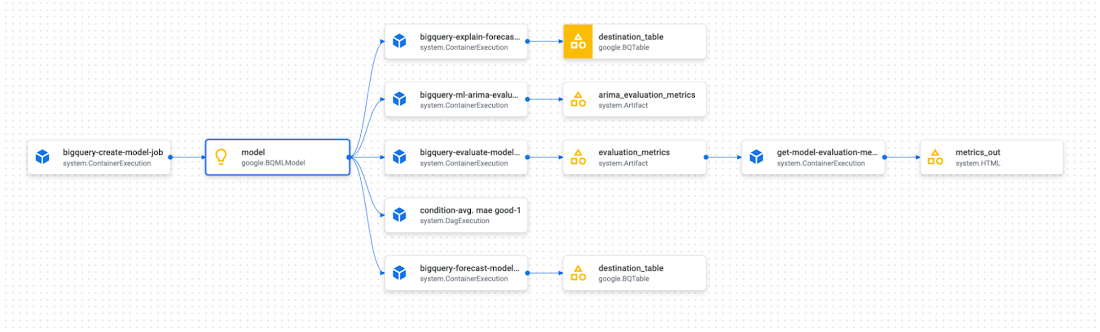
At the end, here you will see the visualization of the overall pipeline you define in the Vertex AI Pipelines UI.
And if you want to analyze, debug, and audit ML pipeline artifacts and their lineage, you can access the following representation in the Vertex ML Metadata by clicking on one of the yellow artifact objects rendered by the Google Cloud console.
Conclusion
In this blogpost, we described the new BigQuery and BigQuery ML (BQML) components now available for Vertex AI Pipelines, enabling data scientists and ML engineers to orchestrate and automate any BigQuery and BigQuery ML functions. We also showed an end-to-end example of using the components for demand forecasting involving BigQuery ML and Vertex AI Pipelines.
What’s next
Are you ready for running your BQML pipeline with Vertex AI Pipelines? Check out the following resources and give it a try:
- Documentation
- Code Labs
- Vertex AI Samples: Github repository
- Video Series: AI Simplified: Vertex AI
- Quick Lab: Build and Deploy Machine Learning Solutions on Vertex AI
References
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/data-analytics/solving-for-food-waste-with-data-analytics-in-google-cloud
- https://cloud.google.com/architecture/build-visualize-demand-forecast-prediction-datastream-dataflow-bigqueryml-looker
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/developers-practitioners/announcing-bigquery-and-bigquery-ml-operators-vertex-ai-pipelines
By: Ivan Nardini (Customer Engineer) and Steve Walker (Customer Engineer, Machine Learning)
Source: Google Cloud Blog
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!