Business partnerships across many industries strain under rules and requirements that prevent them from sharing sensitive data. Organizations also recognize that collaboration can accelerate innovation, but meaningful collaboration can be limited or even prevented by the need to protect intellectual property or regulated data. Rising to meet today’s business challenges can require companies to collaborate across internal company silos, with outside organizations, and across geographies, while pooling and enriching joint data sets in a secure and trusted way.
From our partners:
Challenges with data collaboration
At Google Cloud, we’ve built advanced defenses from the ground up to serve individuals, governments and businesses around the world at massive scale. It’s all part of our vision for invisible security, which enables Google to deliver our customers’ the most trusted cloud. We believe the future of computing in the cloud will shift to private, encrypted services which give users and organizations the confidence that they are in control of their data, without exposing it to anyone.
“Information sharing empowers people,” said Vint Cerf, Vice President and Chief Internet Evangelist at Google. “Information flow is what the Internet is about. Information sharing is power. If you don’t share your ideas, smart people can’t do anything about them, and you’ll remain anonymous and powerless.”
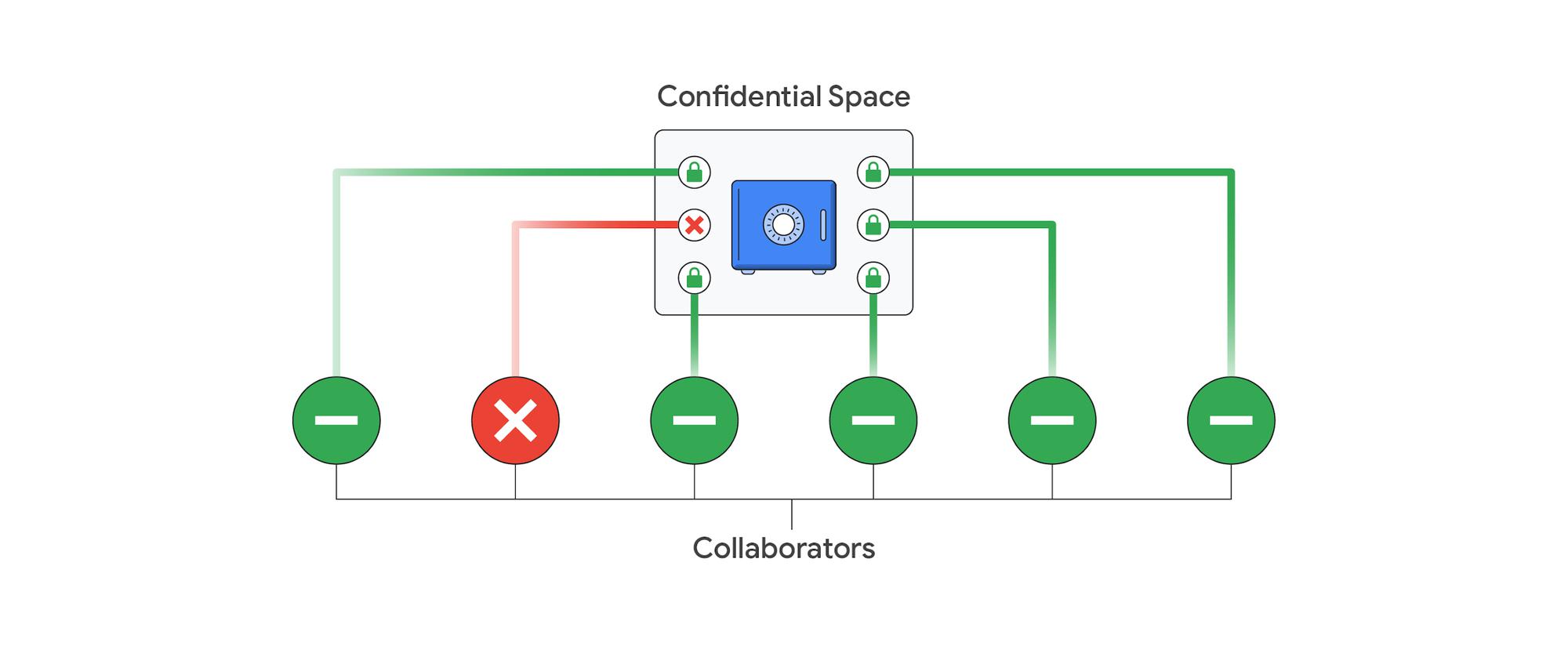
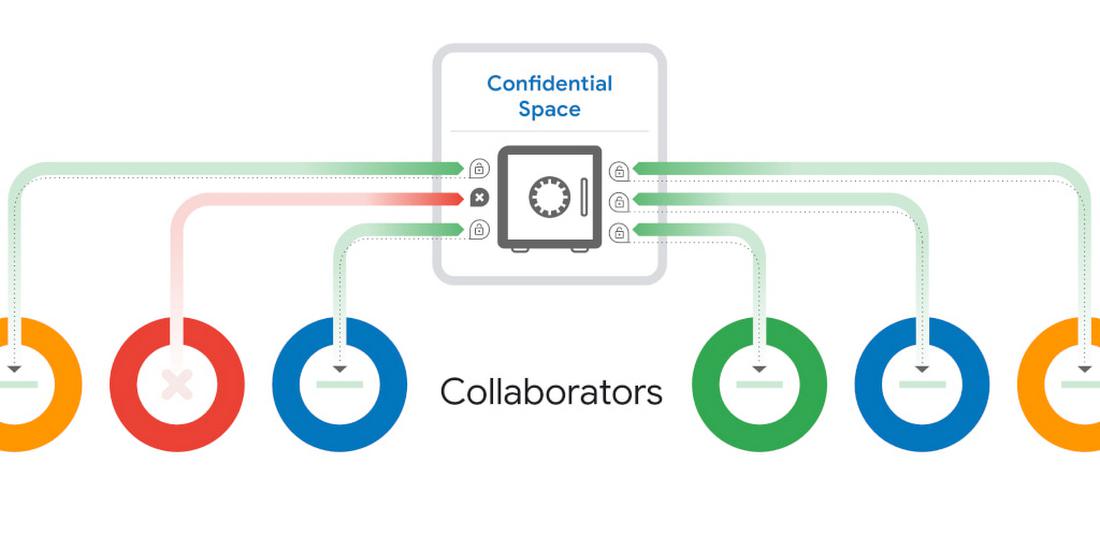
Confidential Space can help ease the tensions between data sharing and regulatory requirements by encouraging collaboration while also maintaining data privacy.
How Confidential Space works
Built on Confidential Computing, and leveraging remote attestation, Confidential Space runs workloads in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). Together with the hardened version of Container-Optimized OS (COS), data contributors can have control over how their data is used and which workloads are authorized to act on it. Finally, Confidential Space blocks the workload operator from influencing the workload in any way.
How you can use Confidential Space
With Confidential Space, organizations can gain mutual value from aggregating and analyzing sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), intellectual property, and cryptographic secrets — while retaining full control over it. This collaboration can lead to innovation, better customer service, and the development of transformational technologies. Here are a few examples that we have discussed with customers that illustrate the broad potential of Confidential Space.
Financial institutions, such as banks and insurance agencies, need to collaborate to identify fraud or detect money laundering activity across their joint customer data set. Confidential Space can make this type of data sharing possible even though the data is highly sensitive, there are strict regulatory requirements, and these organizations often compete with each other. Financial institutions can be sure with Confidential Space that their data is only used for fraud detection while keeping business and confidential information private to the data owner.
“With Confidential Space, our customers don’t have to worry about [data] compromise when sharing data,” said Brendan Taylor, chief technology officer, MonetaGo. “The prevention of fraud helps accelerate growth, which we can achieve while maintaining privacy and enabling critical real-time decision making. Our solution not only helps financial institutions to address the huge amounts of value lost each year due to a lack of information sharing, but most importantly should help millions of businesses get better access to working capital.”
Healthcare and medical technology companies can speed up development of pharmaceuticals and improve diagnostics using machine learning, without compromising patient data or risking non-compliance with international data privacy laws.
Web3 institutions can use Confidential Space to securely and instantly transact digital assets. Relying on multiparty computation (MPC), distributed collaborators can participate in an auditable signing process. Confidential Space’s verifiable attestation can help ensure that all collaborators securely approve while never exposing their private signing keys to other parties, including the platform operator.
Next steps
Confidential Space adds to our growing portfolio of products using Confidential Computing. Earlier this year, we launched to general availability Confidential Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Nodes and extended the flexibility of our Confidential VMs to new instance types. Additionally, Google Cloud Security and Google Project Zero partnered with the AMD firmware and product security teams on an in-depth security audit of the AMD technology that powers Confidential Computing, which you can read here.
By default, Google Cloud keeps all data encrypted, in-transit between customers and our data centers, and at rest. Confidential Computing can extend data privacy by protecting the confidentiality of your data and keeping it encrypted even while it is being processed.
With Confidential Space, we now enable new multi-party collaboration use cases, such as secure data sharing, privacy preserving analytics, and joint ML training. For more information, see our presentation at Next ’22 with Brendan Taylor, CTO at MonetaGo, and sign up for the Preview here.
By: Rene Kolga (Product Manager, Google Cloud) and Nelly Porter (Group Product Manager, Google Cloud)
Source: Google Cloud Blog
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!