What is CI/CD?
Continuous Integration (CI), at its core, is about getting feedback early and often, which makes it possible to identify and correct problems early in the development process. With CI, you integrate your work frequently, often multiple times a day, instead of waiting for one large integration later on. Each integration is verified with an automated build, which enables you to detect integration issues as quickly as possible and reduce problems downstream.
Continuous Delivery (CD) extends CI. CD is about packaging and preparing the software with the goal of delivering incremental changes to users. Deployment strategies such as red/black and canary deployments can help reduce release risk and increase confidence in releases. CD makes the release process safer, lower risk, faster, and, when done well, boring. Once deployments are made painless with CD, developers can focus on writing code, not tweaking deployment scripts.
From our partners:
How has the application development landscape changed?
Much has changed in the app development space recently, and you’ll want to take these changes into account as part of your CI/CD strategy.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud deployments – Large enterprises want to deploy applications in hybrid cloud environments, with tools and services that don’t lock them into a specific vendor.
- The shift from monolith to microservices – Teams are breaking down large monoliths into microservices for greater agility. This makes it possible for different teams to use different languages, tech stacks, development lifecycles, which means deployment patterns, tooling needs, and scaling patterns are changing.
- Cloud-native applications – It’s not just VMs anymore; companies are shifting paradigms and embracing serverless, containers, and Kubernetes. While simplifying some aspects of app development, this move adds complexity in other areas. How do you handle rollbacks? Canary deployments? It’s different now.
Ideally, developers should be focused on their code, not on ushering their changes through a CI/CD process. CI/CD steps should be triggered and run behind the scenes as soon as code is checked in. So, your CI/CD pipeline should support:
- Packaging source code
- Automated unit and integration tests
- Consistent build environments
- Approvals before deploying to production
- Blue/green and canary roll-outs
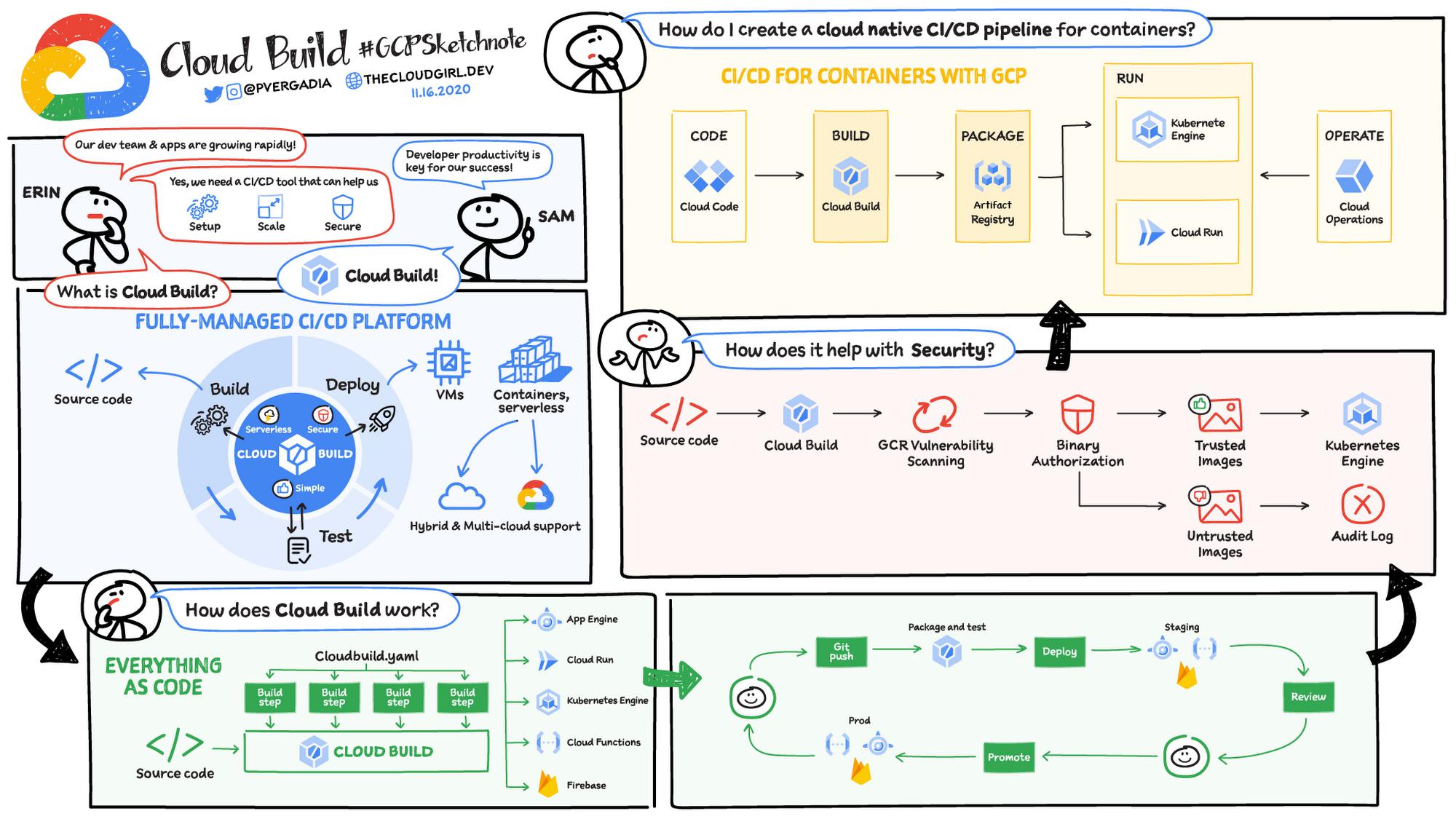
That’s where Cloud Build comes in.
Google Cloud DevOps overview
Cloud Build
Cloud Build is a fully-managed CI/CD platform that lets you build, test, and deploy across hybrid and multi-cloud environments that include VMs, serverless, Kubernetes, and Firebase. Cloud Build can import source code from Cloud Storage, Cloud Source Repositories, GitHub, or Bitbucket; execute a build to your specifications; and produce artifacts such as Docker container images or Java archives.
Cloud Build executes your build as a series of build steps, with each step run in a Docker container. A build step can do anything that can be done from a container irrespective of the environment. To perform your tasks, you can either use the supported build steps provided by Cloud Build or write your own build steps. As a part of the build step, Cloud Build deploys the app to a platform of your choice. You also have the ability to perform deep security scans within the CI/CD pipeline using Binary Authorization and ensure only trusted container images are deployed to production.
Cloud Build private pools help you meet enterprise security and compliance requirements. These are private, dedicated pools of workers that offer greater customization over the build environment, including the ability to access resources in a private network. For instance, you can trigger fully managed DevOps workflows from source code repositories hosted in private networks, including Github Enterprise.
Cloud Code
If you are working entirely in a cloud-native environment, then you’ll want to use Cloud Code to kick off your CI/CD pipeline. Use Cloud Code in your IDE; it comes with tools to help you write, run, and debug cloud-native applications quickly and easily. Then push your code to Cloud Build for the build process, package it in the Artifact Registry, and run it on GKE or Cloud Run. You can get all the visibility and metrics you want for the deployment in Google Cloud’s operations suite.
Cloud Deploy
Google Cloud Deploy (in preview) is a managed, opinionated continuous delivery service that makes continuous delivery to GKE easier, faster, and more reliable. It has built in security controls and it can be integrated with your existing DevOps ecosystem.
Cloud Shell Editor
Cloud Shell Editor, powered by the Eclipse Theia IDE platform, extends Cloud Shell with an online preconfigured cloud development environment that includes:
- Local emulators for Kubernetes and serverless, and
- Command line tools for working with cloud-native apps
Interested in getting started with CI/CD on Google Cloud? Check out the documentation here. For more #GCPSketchnote and similar cloud content, follow me on twitter @pvergadia and keep an eye out on thecloudgirl.dev
By: Priyanka Vergadia (Developer Advocate, Google)
Source: Google Cloud Blog
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!