The kinds of observability data provided
gRPC observability provides three different types of data:
From our partners:
1. Logs for key RPC events, including:
- When the client/server sends or receives the metadata of an RPC
- When the client/server sends or receives the message payload of an RPC
- When the client/server finishes an RPC with a final status (OK, or errors)
2. Metrics (or statistical data) for key RPC events, including:
- How many bytes the client/server sent or received
- How many RPCs the client/server started or completed
- How long RPCs take to complete between the client and server (known as round trip latency)
3. Distributed traces for RPCs and their fanout RPCs across the system. For example, when serving an RPC from upstream, a server may need to create multiple RPCs to its own backends. The distributed trace helps the user understand the relationships between these RPCs, the latency for each of them, and key events happening throughout the system.
How the observability data is produced and collected
When developers enable the gRPC observability feature in their binaries, the gRPC library will report the logging, metrics, and tracing data to Google Cloud’s operations suite. Once the observability data is collected, users can leverage the Google Cloud console to:
- Visualize the observability data
- Export the observability data out of the operations tools for further analysis with other tools.
Logging
gRPC observability provides logs for key RPC events with information to help developers understand the context when these events occur. This contextual information can include which gRPC service/method is being invoked, whether the events happen on the client side or server side, whether it’s sending metadata or payloads, the size of the corresponding data, and even the concrete content of the metadata and/or payloads. These log entries are then presented in Cloud Logging with helpers to filter and even customize the query to search related logs.
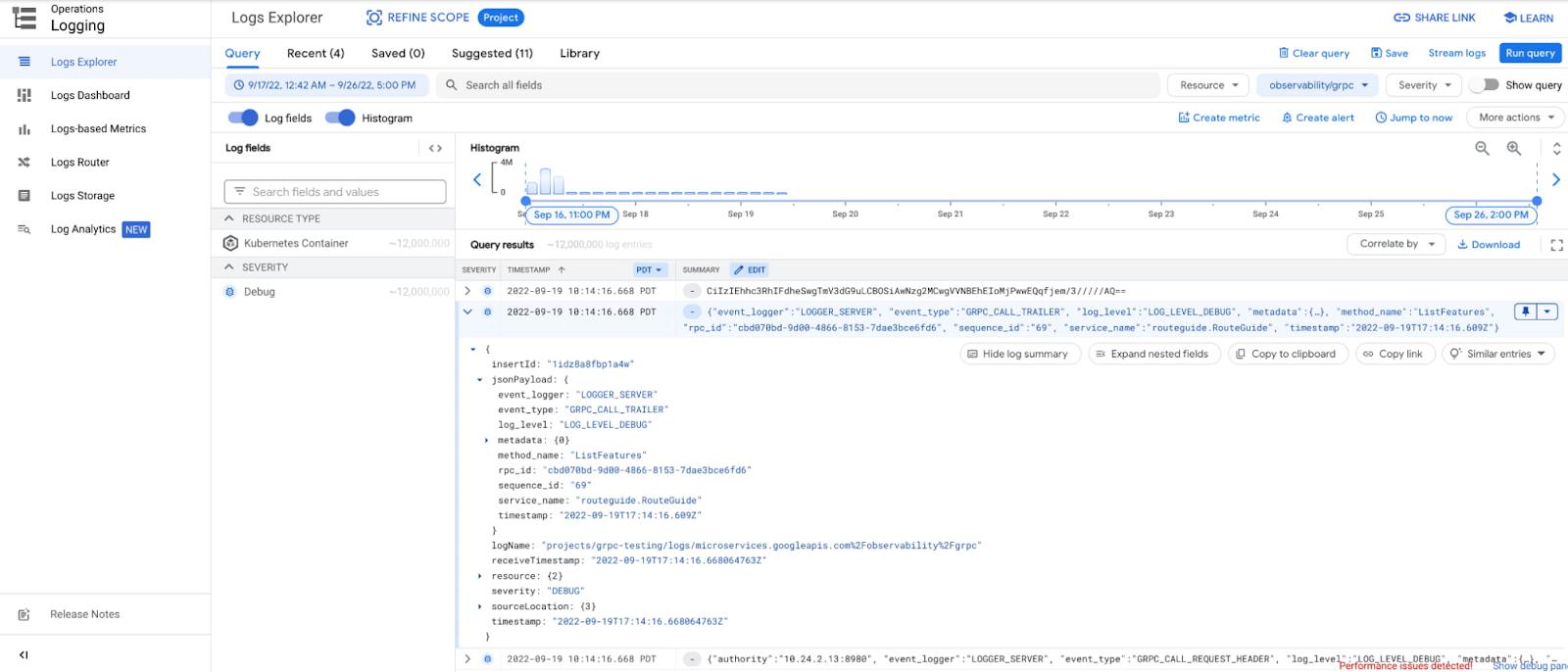
- Which container is having higher than normal latency
- Which pod is having higher than normal error rates
- And others.
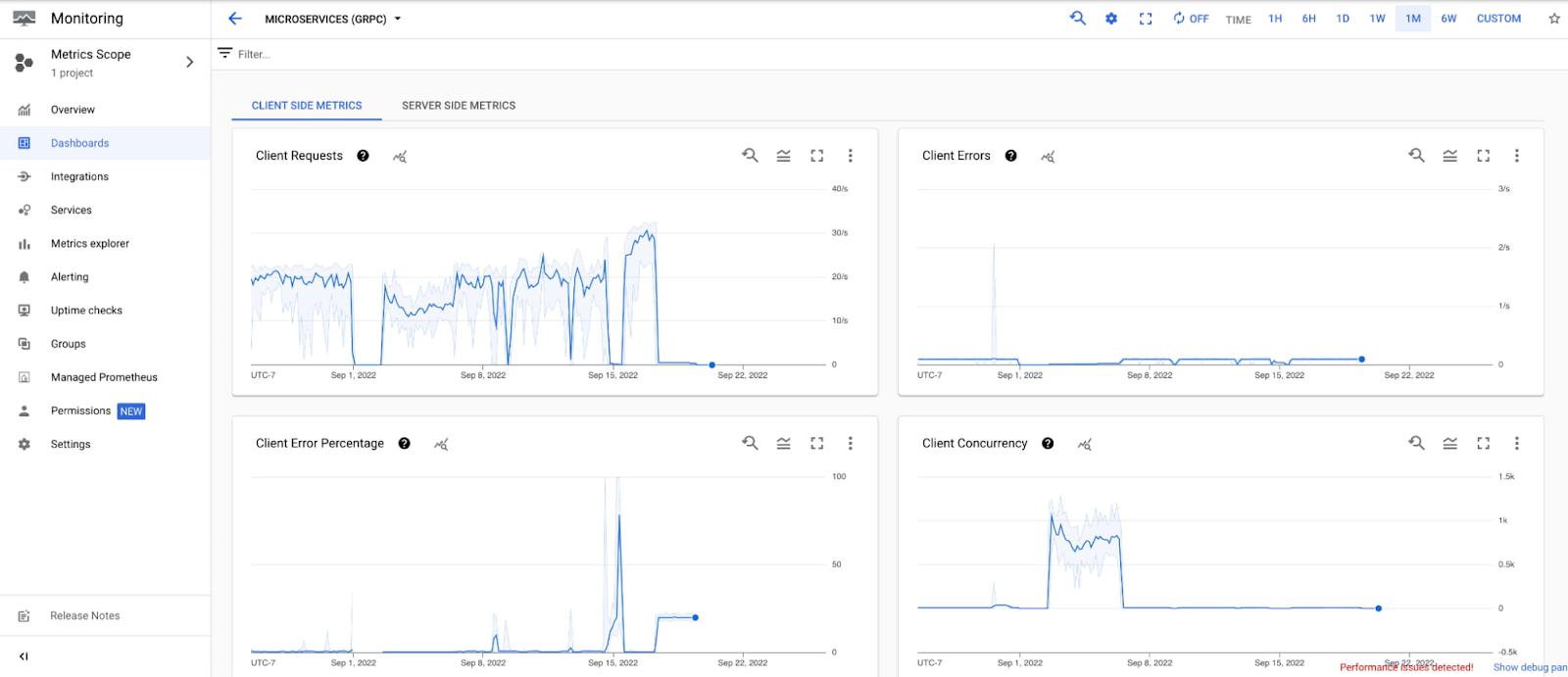
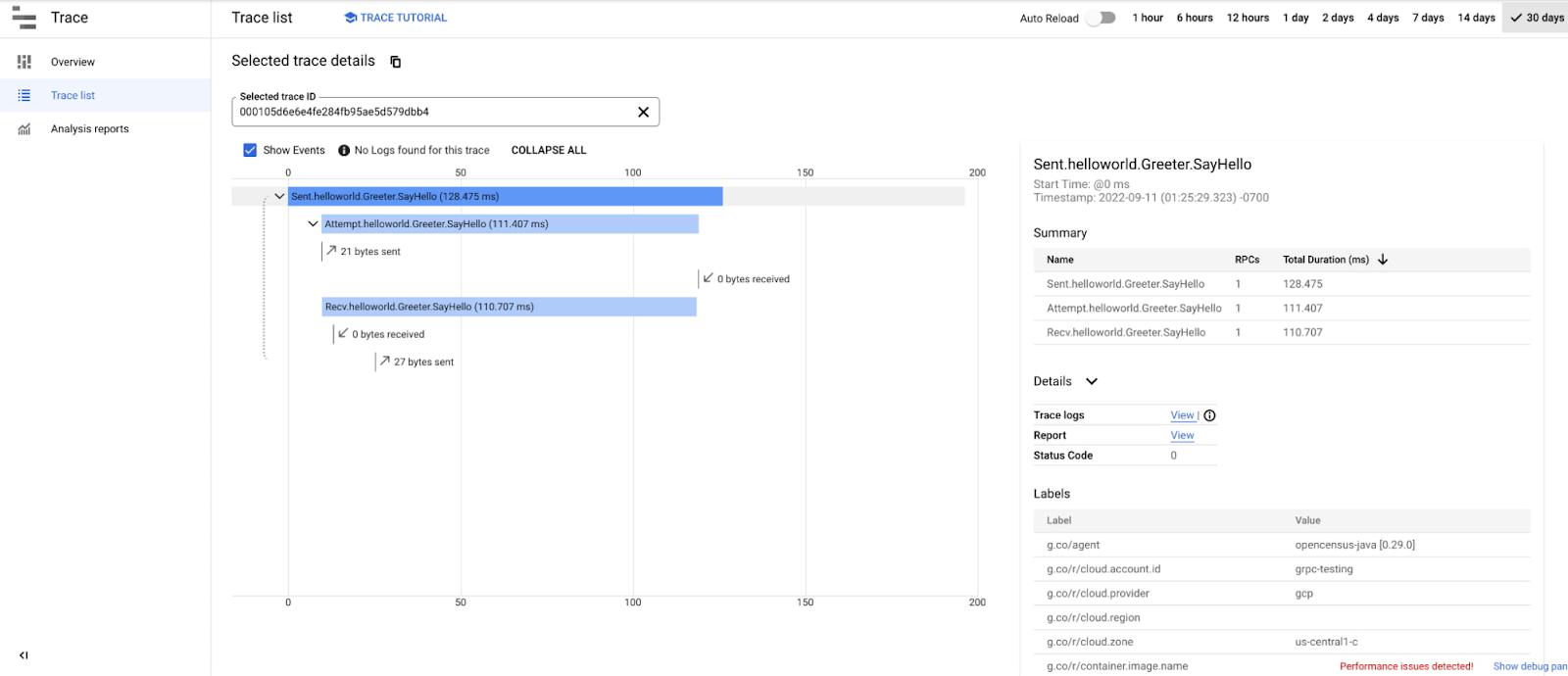
Getting started
With gRPC observability, telemetry data (logs, metrics, traces) of gRPC workloads can be collected and reported to the Google Cloud operations suite. It helps developers get a better understanding of their systems and enables them to diagnose problems such as:
- Which microservices have suddenly become abnormally slow (long processing latency on the server side)?
- Which microservices suddenly process less QPS, and is there a pattern?
- Whether there’s a potential network issue for a particular microservice, as high latency is measured on the client side, but normal latency on the server side? If so, can we locate the problem in a particular cluster, or even a particular node/pod?
To get started with gRPC observability, see our user guide.
By: Feng Li (Software Engineer, Google)
Source: Google Cloud Blog
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!






