The 5th generation of mobile communications, 5G has arrived and it has brought us mostly higher throughputs and helped operators to satisfy the ever-increasing demand for mobile data traffic. This first wave of 5G uses the so-called “non-standalone mode”, which means that it still depends on existing 4G networks for coverage and control, so some of the advanced features of 5G are not yet available.
Operators are already working on the roll out of the second wave of 5G, which will be able to operate in a standalone mode, independently of 4G. Only this standalone mode will be able to reduce the latency of the network (the delay between the user’s data request and the actual delivery of that data) and will thus be able to support applications like augmented reality, e-health, and cooperative cars.
From our partners:
Another advantage of standalone 5G is the possibility to deploy private 5G networks for specific use cases, such as industrial automation, where robots and vehicles need to be controlled in real-time. This time-sensitive communication requires high speed and reliability that today’s 4G and wifi networks, despite being state of the art, are not able to deliver.
However, today’s 5G equipment is much more expensive than its 4G counterpart, especially the part called “radio access network” (RAN), which serves to communicate between terminals using radio waves. Building private 5G deployments is thus very pricey. Moreover, today there are only a handful of manufacturers of RAN equipment and their products are, as is traditional in the industry, proprietary and closed, making it hard to adapt them to specific requirements of private 5G networks.
Opening up Radio Access Network equipment
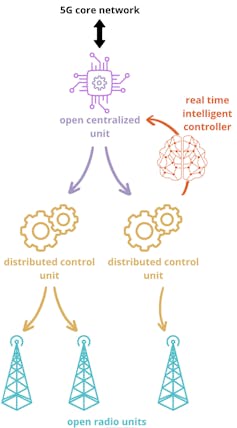
One promising solution to these problems is the “open RAN architecture”. This breaks down the traditional components of a RAN into a few smaller components, with openly defined interfaces between them (see Figure 1). This “split architecture” allows more flexible deployments that can be adapted to different use cases, such as low latency or high throughput.
Further, the open RAN design introduces the so-called RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC), which can be used to control and optimize the RAN in an intelligent, agile, and programmable way. This can be used for example to optimize the quality of service or quality of experience for different user groups with different requirements (such as video streaming or gaming), optimize coverage and network throughput by traffic steering or coverage optimization. In doing so, the intelligent controller can also exploit feedback from the RAN and use methods from machine learning and artificial intelligence for optimization.
In an open RAN design, interfaces between the different elements as well as real-time control and management and operation are openly defined by standardization bodies such as the O-RAN Alliance or the 3rd generation partnership project 3GPP. This makes is possible to mix and match components from potentially different vendors, thus increasing competition and reducing costs. It also reduces the dependency of a customer on a vendor for products, so he can easily switch to another, potentially cheaper, vendor.
Elsa Couderc, Florian Kaltenberger
Increased use of open-source software
Another key advantage of the open RAN architecture is that all the elements – except for the radio unit – can be implemented as “virtual network functions” – that is, software – that can potentially run on general-purpose computing and networking environments, or even on the cloud. Such deployments are thus sometime called “virtualized RAN” or “cloud RAN”. This makes it possible to deploy such networks on existing IT infrastructure of factories, business parks or hospitals, which is another important cost-reducing factor.
Since virtual network functions are basically software, the next natural step to bring down costs is to use open-source software for these functions. Open source has already penetrated much of mobile radio networks. Indeed, the majority of smartphones today use Android as an operating system, which is based on open-source Linux. There is also a plethora of open-source software available to run and manage cloud and telecom environments.
On the side of the RAN, the OpenAirInterface (OAI) project is worth mentioning as it is the most complete implementation of 5G networks today and lets you run a complete network on general purpose computing and radio infrastructure. Initially created for academic and research purposes, it is currently gaining significant traction and is finding its way into some products. However, there is still some work to make it compatible to O-RAN specifications and to improve the stability to make it ready for real deployments.
Open source is also a very good method to increase security and trust into mobile networks. Most open-source projects are managed by independent non-profit organizations, which continuously test and analyze the code for functionality, performance and security, so it is hard to introduce potential security threats and backdoors.
Last, but not least, open source software makes it easier for new players and startups to enter the 5G market, as they do not have to develop their products from scratch and benefit from other developments in the community. More startups also means more innovation and competition and thus will ultimately bring down the costs of private 5G even more. Think of how the Android operating system, which is also open source, resulted in the creation a wide range of new and cheaper mobile devices.
Open RAN products are still in their infancy and not yet ready for large-scale commercial deployments, but there are however promising field trials happening in different parts of the world. For example, the French operator Orange is has deployed an experimental open RAN network in Lannion and Chatillon. Moreover, different studies suggest that the open RAN market will outgrow the traditional RAN market for private 5G networks as early as 2024 and for public networks around 2030.
In conclusion, open RAN and open source are a perfect combination to bring down costs of 5G networks while at the same time providing contributing to build sovereign networks that are independent of a particular vendor.![]()
Florian Kaltenberger, Associate professor en communications sans fils, EURECOM, Institut Mines-Télécom (IMT)
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license.
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!




