The Best Sunday of Summer!
Managed Service for Prometheus and Cloud Monitoring
Prometheus is a multidimensional monitoring and alerting data model with time series data identified by metric name and key/value pairs. Google Cloud Managed Service for Prometheus is Google Cloud’s fully managed multi-cloud solution for Prometheus metrics. Managed Service for Prometheus lets you globally monitor and alert on your workloads, using Prometheus, without having to manually manage and operate Prometheus at scale.
From our partners:
3 reasons why it’s one of my favorite services:
1. Managed Service for Prometheus is built on top of Monarch, the same globally scalable data store used for Google’s own monitoring, and it uses the same backend and APIs as Cloud Monitoring
2. All Cloud Monitoring metric data is queryable using PromQL, and all Managed Service for Prometheus data is queryable using Cloud Monitoring
3. You can use PromQL to query over 1,500 free metrics in Cloud Monitoring, even without sending data to Managed Service for Prometheus
Let’s see a quick overview of accessing Managed Service for Prometheus data in different ways:
Monitoring with Metrics Explorer
1. In the Google Cloud Console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project
2. Make sure that billing is enabled for your Cloud project. Learn how to check if billing is enabled on a project
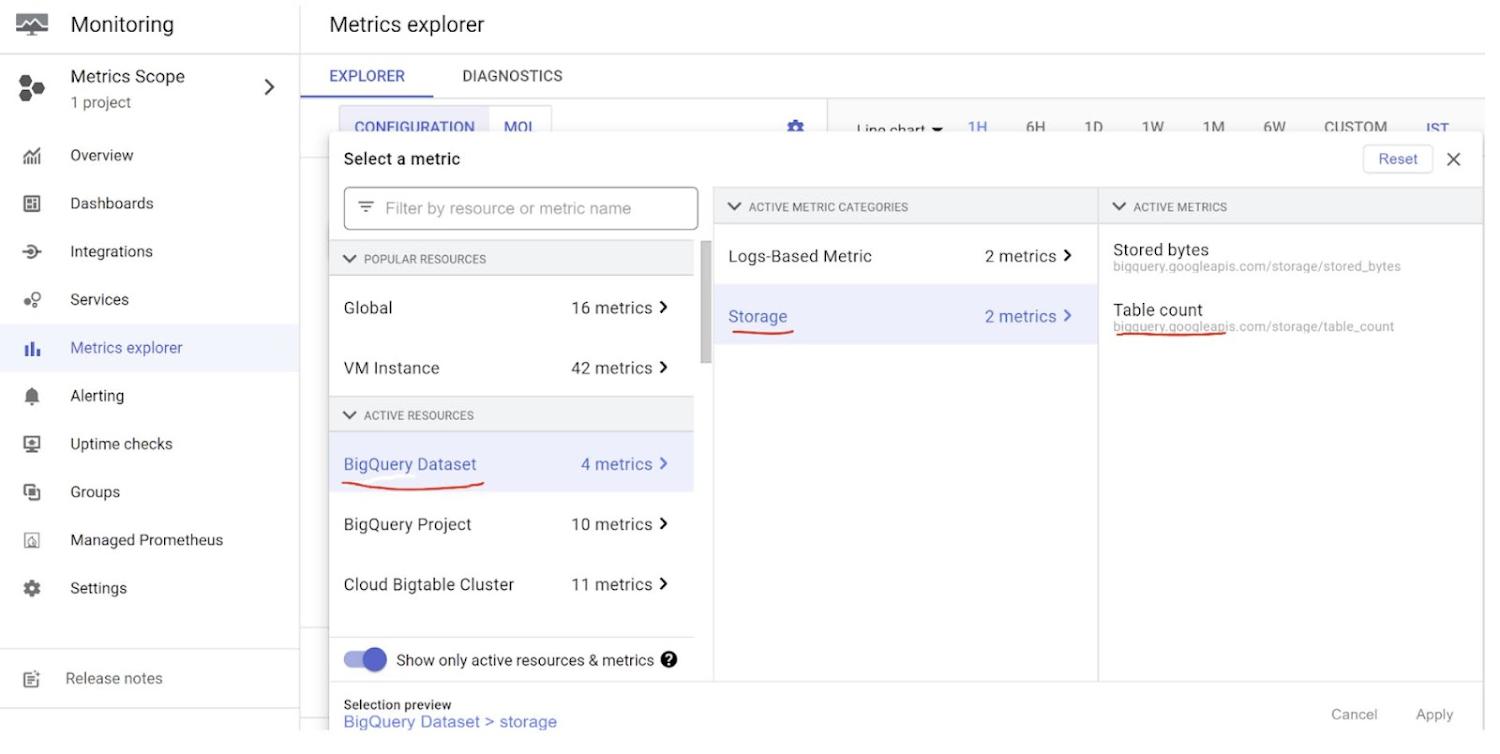
3. Navigate to Managed Prometheus by searching for it in the Google Cloud Console and let’s view the Storage Metrics of my BigQuery Usage
4. Click Metrics Explorer and click on “Select a Metric”
5. Navigate to BigQuery Dataset in the list that pops up
6. Select Storage from the list of Active Metric Categories list
7. Click Apply
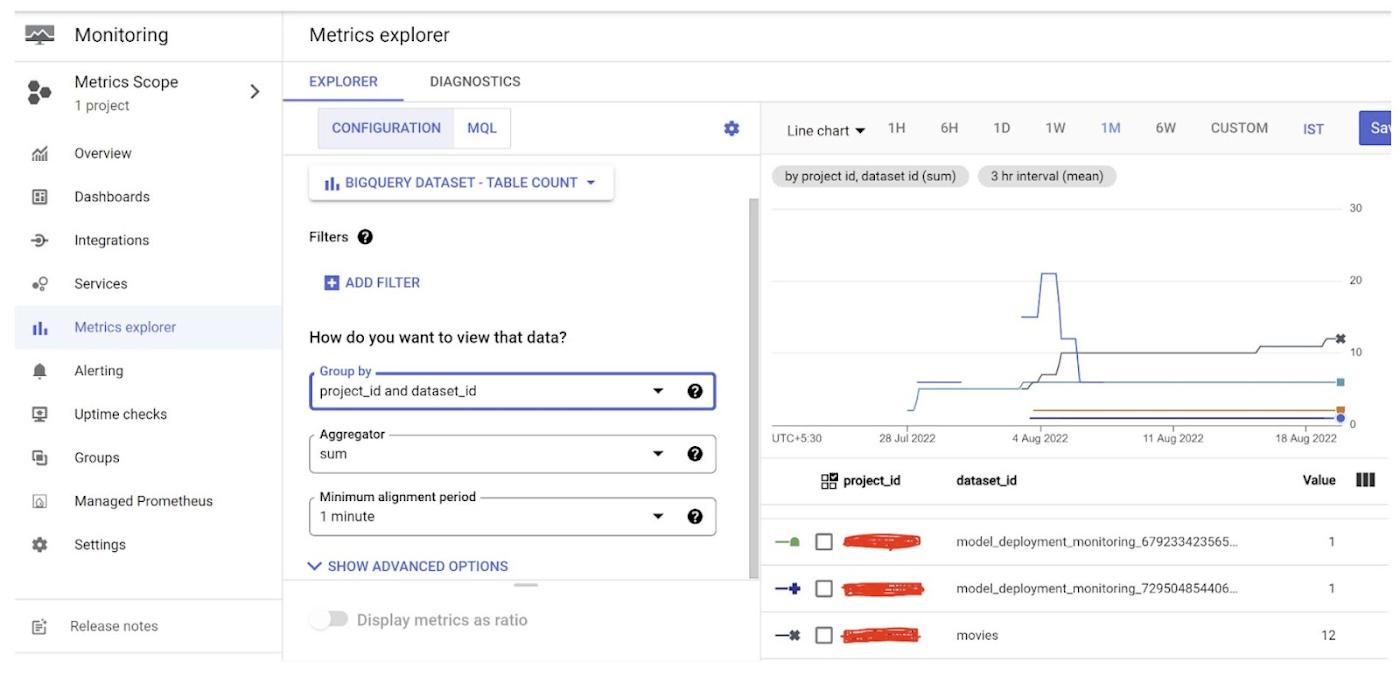
9. On the left, you will see Configuration and MQL (Monitoring Query Language) tabs
Note: This is as-of-now. An important update is expected to come next month to the Query Language section of Cloud Monitoring and the update will also be published in this blog next month10. In configuration tab, you can configure some settings includinga. Group by fields
b. Aggregator
c. Alignment Period
d. Legend template etc.
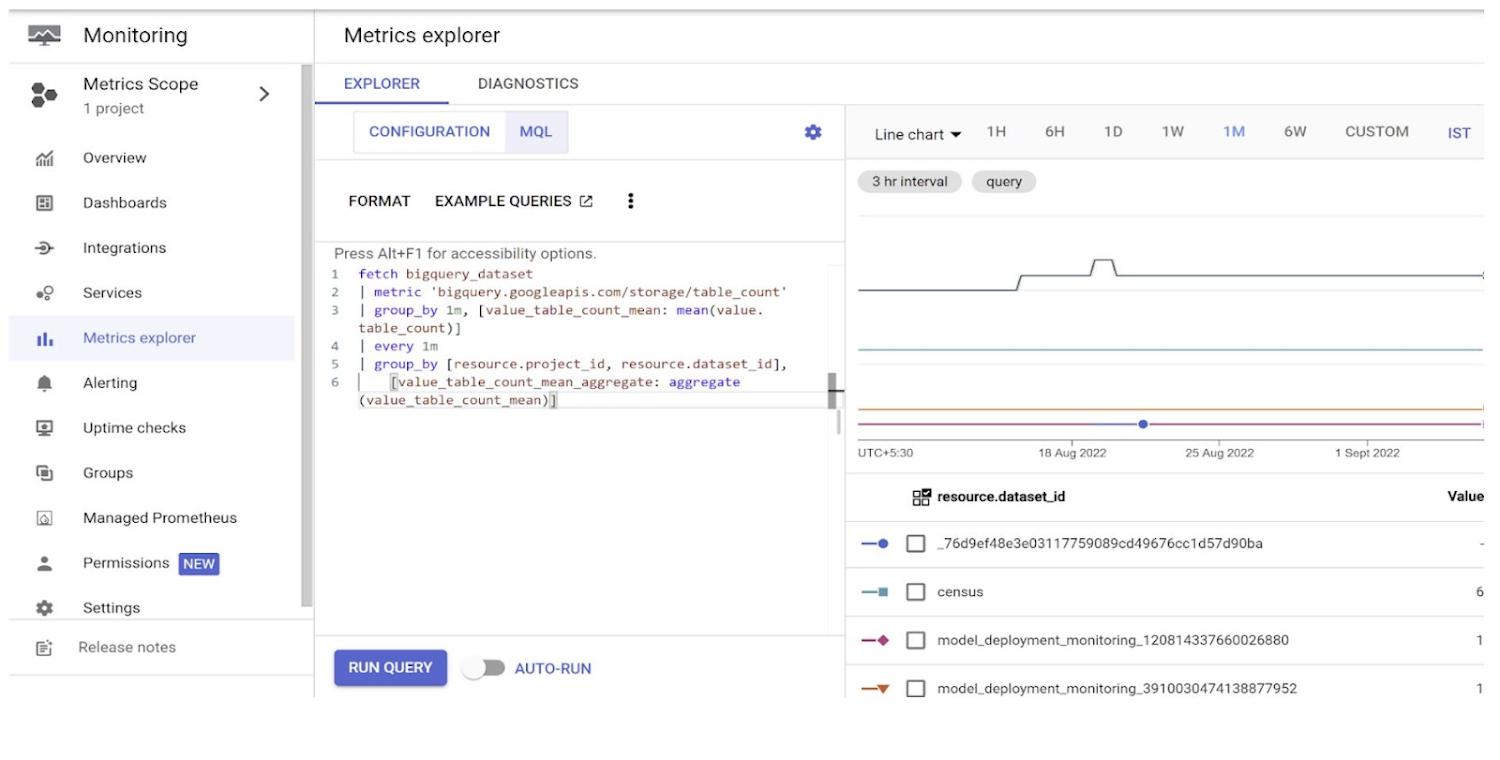
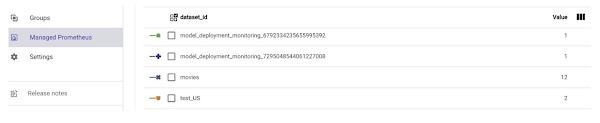
12. As you can see below, in this demo, I have taken Project Id and Data Set Id as the Group by fields and Sum as the aggregator:
fetch bigquery_dataset
| metric 'bigquery.googleapis.com/storage/table_count'
| group_by 1m, [value_table_count_mean: mean(value.table_count)]
| every 1m
| group_by [resource.project_id, resource.dataset_id],
[value_table_count_mean_aggregate: aggregate(value_table_count_mean)]
Managed Service for Prometheus with PromQL
I love this part where you can click a button to land on a page that lets you query both Google Cloud Managed Service for Prometheus metrics and Cloud Monitoring metrics.
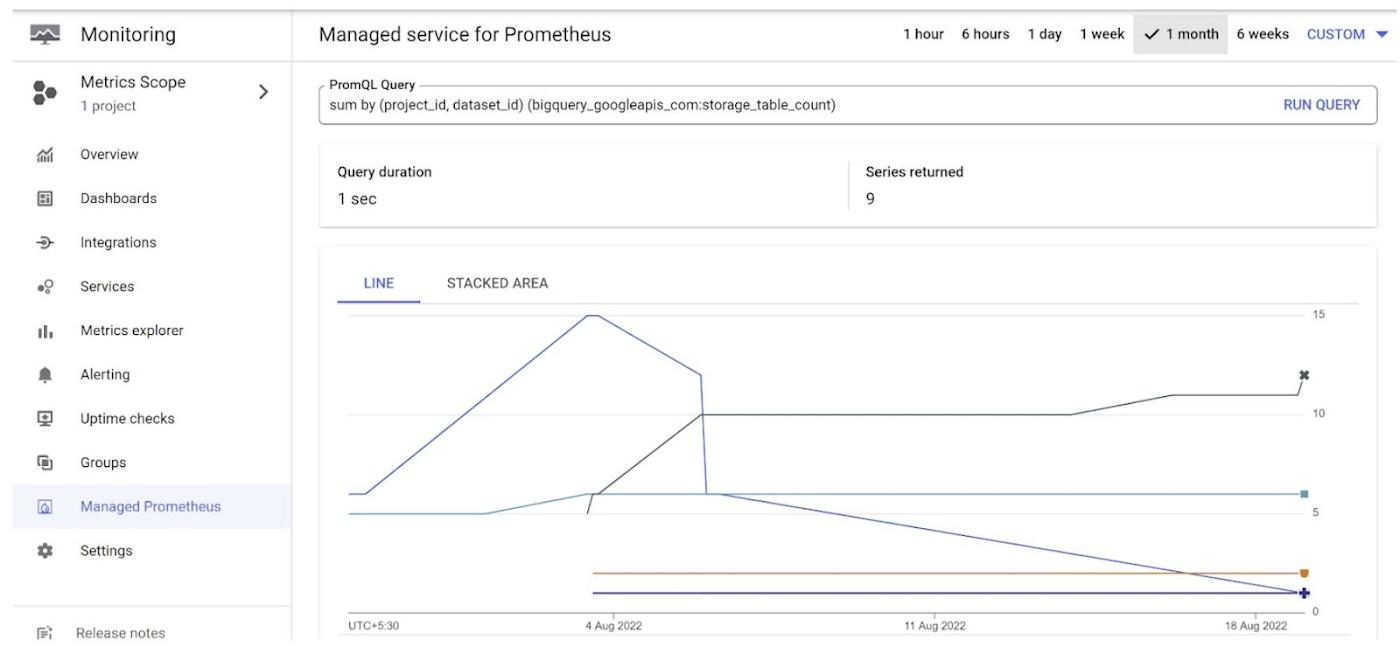
2. In this case, we are calculating the sum of tables grouped by dataset and projectPromQL:
sum by (project_id, dataset_id) (bigquery_googleapis_com:storage_table_count)
4. There is more to Managed Service for Prometheus on Google Cloud like setting Alerting Policies, Rules, Integrations to other services and tools than the 2 demonstrations I have addressed here, refer to the documentation to get started
Cloud Monitoring in GROUPS
There is one favorite feature that I want to call out as part of this section and that is the GROUPS feature inherent to Cloud Monitoring that lets you define and monitor groups of resources, such as VM instances, databases, and load balancers and you can organize resources into groups based on criteria that make sense for your applications.
Imagine all your resources, applications, databases, dependencies and other services being monitored in a single-pane-of-glass-view without having to access multiple reports and maintain several storages. That is what the GROUPS feature of Cloud Monitoring service lets you do.
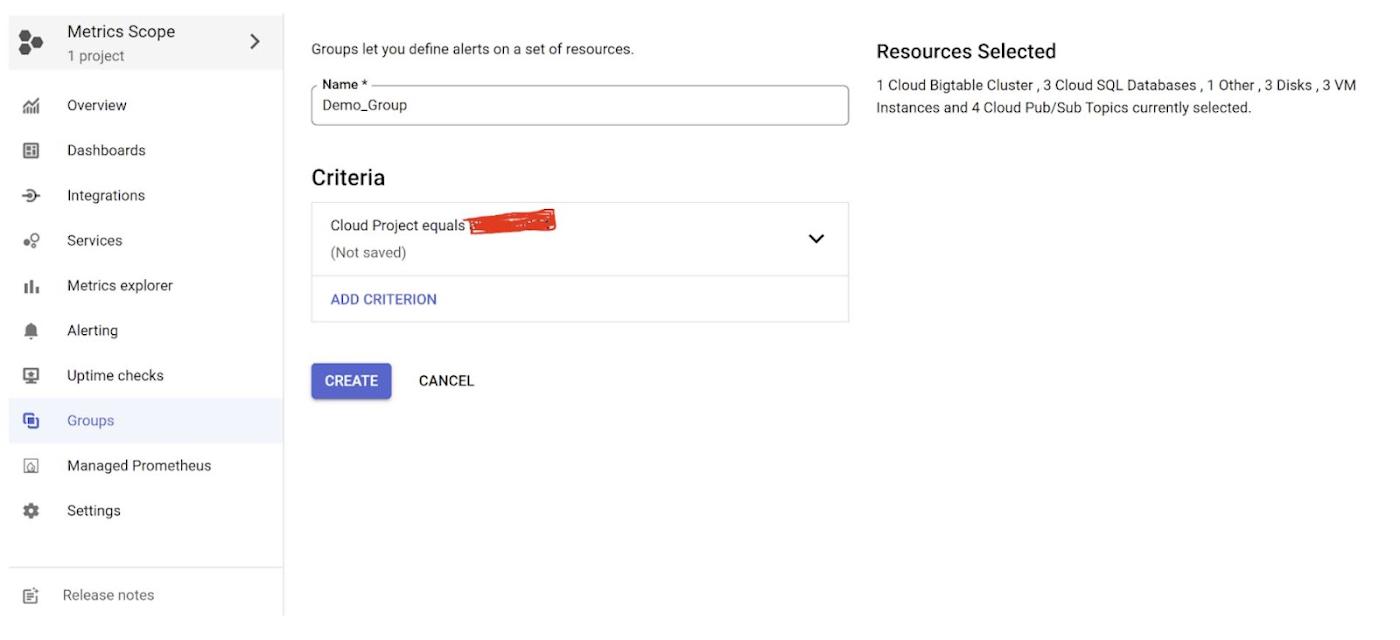
a. On the monitoring console, click “Groups” on the left
b. Enter your Group Name
c. Select the criteria for your group
d. Click CREATE
Monitoring Access Permissions
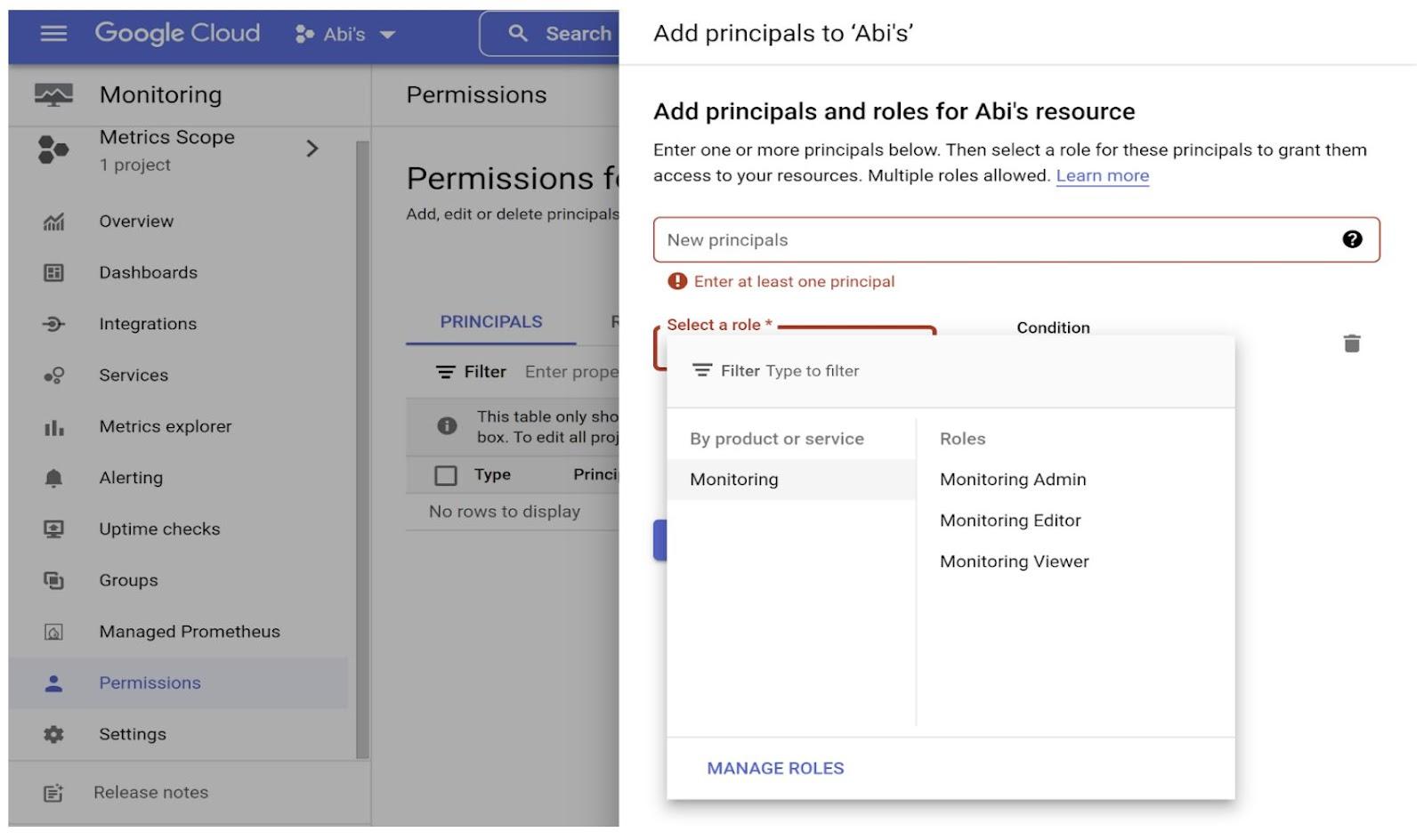
With the new Permissions tab for Monitoring access, you are able to add, edit and delete principals to modify Monitoring access for this project. This way you are able to control Monitoring Admin, Editor and Viewer access for monitoring all your resources and services in one place.
1. Click ‘Permissions’ link on the left bottom section of the Cloud Monitoring console
2. On the right, you would be able to add and remove Permissions with Principals and Roles as shown in the screenshot below
Serverless MongoDB Atlas on Google Cloud
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed, global cloud database from MongoDB that combines a flexible JSONâ€like data model, rich querying and indexing, and elastic scalability while automating timeâ€consuming database admin tasks. MongoDB Atlas provides customers a fully managed service on Google’s globally scalable and reliable infrastructure. Atlas allows you to manage your databases easily with just a few clicks in the UI or an API call, is easy to migrate to, and offers advanced features such as global clusters for low-latency read and write access anywhere in the world. We can easily deploy, manage and grow MongoDB on Google Cloud, integrate with Cloud Key Management Service to manage sensitive data, migrate existing MongoDB applications to cloud with other Google Cloud native experience and the very interesting aspect of it all – take advantage of Google’s ML and AI capabilities with the MongoDB application.
Did you hear Serverless?
You heard it right! As modern application developers, we’re juggling many priorities: performance, flexibility, usability, security, reliability, and maintainability. On top of that, we’re handling dependencies, configuration, and deployment of multiple components in multiple environments and sometimes multiple repositories as well. And then we have to keep things secure and simple. Ah, the nightmare!
This is the reason we love serverless computing. Serverless allows developers to focus on the thing they like to do the most—development—and leave the rest of the attributes, including infrastructure and maintenance, to the platform offerings. However, many serverless models overlook the fact that traditional databases are not managed. You need to manually provision infrastructure (vertical scaling) or add more servers (horizontal scaling) to scale the database. This introduces a bottleneck in your serverless architecture and can lead to performance issues.
MongoDB launched serverless instances, a new fully managed, serverless database deployment in Atlas to solve this problem. With serverless instances you never have to think about infrastructure — simply deploy your database and it will scale up and down seamlessly based on demand — requiring no hands-on management. And the best part, you will only be charged for the operations you run.
You can refer to the blog linked here to create, build and deploy a fully serverless MEAN (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular.js, Node.js) stack application with Google Cloud Run and MongoDB Atlas on Google Cloud.
Conclusion
That–my friends–is our celebratory conclusion of the 7-part blog series. Thank you for taking the journey with me. You can try your hands on the experiments I had included in part of this series and see the consolidated list of database blogs here and reach out if you have specific topics of interest. Here are some links you can reference to learn more about Cloud Monitoring Insights, Query Insights, Prometheus and more:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7BLV24noNGc
https://cloud.google.com/monitoring
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VL2Ql0cmo4g&autoplay=1
https://cloud.google.com/products/operations
https://cloud.google.com/managed-prometheus
Please refer to the links below for the all the parts of this blog series:
Databases on Google Cloud: Part 1 – Data modeling basics
Databases on Google Cloud Part 2 – Options at a glance!
Databases on Google Cloud part 3 – Cloud Spanner! & CRUD it with Spring Boot on Cloud Run
Databases on Google Cloud Part 4: Query, Index, CRUD and Crush your Java app with Firestore APIs
Databases on Google Cloud Part 5: Lightweight Application Development with Cloud Functions (Java) and Cloud SQL (SQL Server) in 2 minutes
Databases on Google Cloud Part 6: BigQuery and No-code SQL-only Machine Learning
By: Abirami Sukumaran (Developer Advocate, Google)
Source: Google Cloud Blog
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!