In the ever-evolving world of Linux, where the command line reigns supreme, reviewing Linux commands periodically is like honing the edge of a mighty sword. It’s the secret sauce that keeps your skills sharp, your fingertips nimble, and your sysadmin game strong. Because let’s face it, constantly referring to documentation is like navigating a maze blindfolded—frustrating and time-consuming.
So, embrace the wisdom of the penguin, my friends, and make it a habit to revisit those command-line gems. Unleash the power of your terminal, bask in the elegance of one-liners, and command your Linux kingdom with confidence. Trust me, your fellow geeks will marvel at your mastery, and you’ll be the hero of the command line universe.
From our partners:
These commands are commonly used in Linux systems and cover a wide range of tasks, including file management, process management, system administration, network configuration, and more.
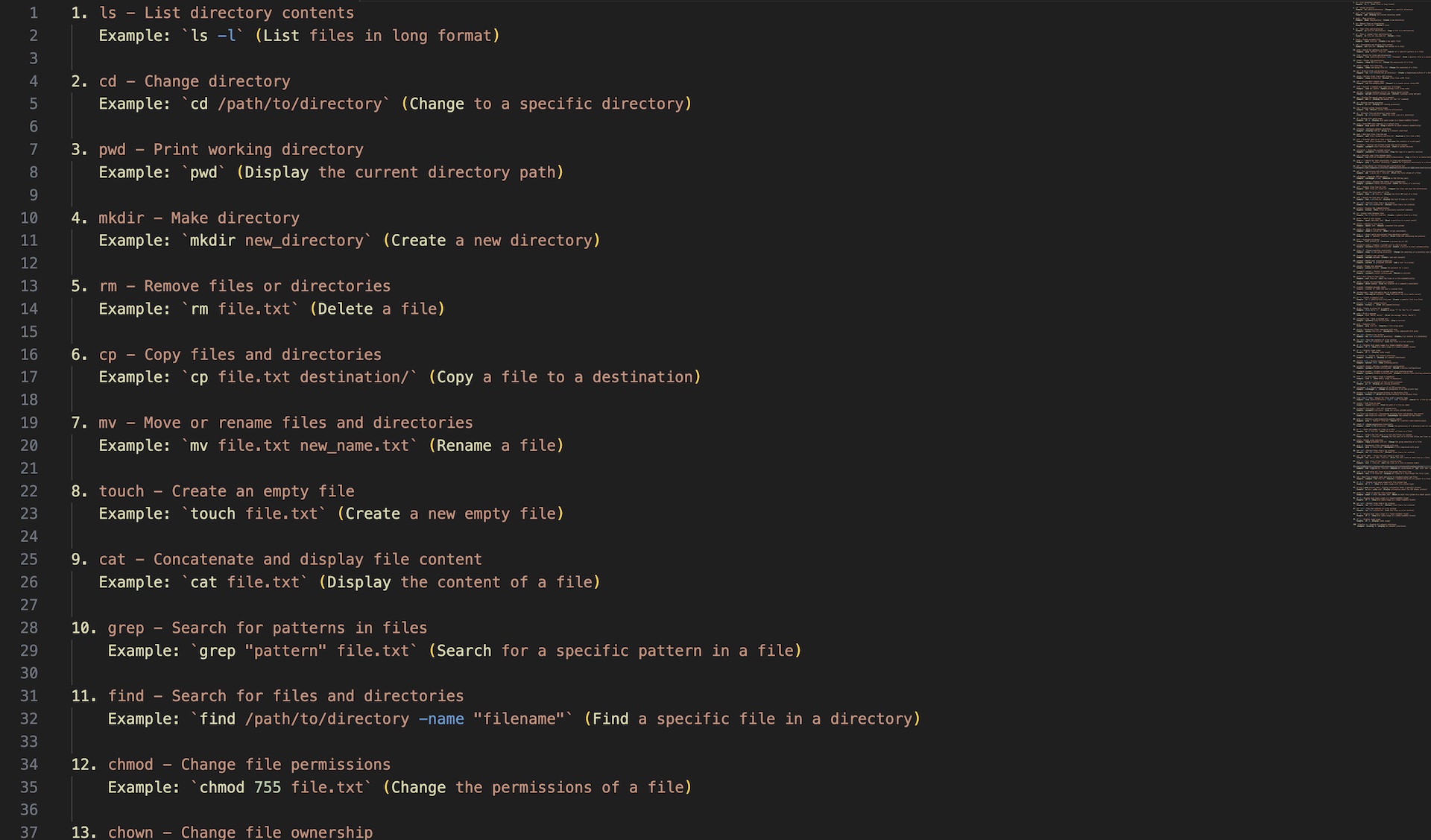
1. ls - List directory contents
Example: `ls -l` (List files in long format)
2. cd - Change directory
Example: `cd /path/to/directory` (Change to a specific directory)
3. pwd - Print working directory
Example: `pwd` (Display the current directory path)
4. mkdir - Make directory
Example: `mkdir new_directory` (Create a new directory)
5. rm - Remove files or directories
Example: `rm file.txt` (Delete a file)
6. cp - Copy files and directories
Example: `cp file.txt destination/` (Copy a file to a destination)
7. mv - Move or rename files and directories
Example: `mv file.txt new_name.txt` (Rename a file)
8. touch - Create an empty file
Example: `touch file.txt` (Create a new empty file)
9. cat - Concatenate and display file content
Example: `cat file.txt` (Display the content of a file)
10. grep - Search for patterns in files
Example: `grep "pattern" file.txt` (Search for a specific pattern in a file)
11. find - Search for files and directories
Example: `find /path/to/directory -name "filename"` (Find a specific file in a directory)
12. chmod - Change file permissions
Example: `chmod 755 file.txt` (Change the permissions of a file)
13. chown - Change file ownership
Example: `chown user:group file.txt` (Change the ownership of a file)
14. tar - Archive files and directories
Example: `tar -czvf archive.tar.gz directory/` (Create a compressed archive of a directory)
15. unzip - Extract files from a ZIP archive
Example: `unzip archive.zip` (Extract files from a ZIP file)
16. ssh - Secure shell remote login
Example: `ssh username@hostname` (Connect to a remote server using SSH)
17. sudo - Execute a command with superuser privileges
Example: `sudo apt update` (Update package lists using sudo)
18. apt-get - Package handling utility for Debian-based systems
Example: `apt-get install package_name` (Install a package using apt-get)
19. man - Display the manual page of a command
Example: `man ls` (Display the manual for the "ls" command)
20. ps - Display running processes
Example: `ps aux` (Display all running processes)
21. top - Display system resource usage
Example: `top` (Monitor system resource utilization)
22. du - Estimate file and directory space usage
Example: `du -sh directory/` (Show the total size of a directory)
23. df - Display disk space usage
Example: `df -h` (Display disk space usage in a human-readable format)
24. ping - Send ICMP echo requests to a network host
Example: `ping google.com` (Ping a website to check network connectivity)
25. ifconfig - Configure network interfaces
Example: `ifconfig eth0 up` (Bring up a network interface)
26. wget - Retrieve files from the web
Example: `wget http://example.com/file.txt` (Download a file from a URL)
27. curl - Transfer data to or from a server
Example: `curl http://example.com` (Retrieve the contents of a web page)
28. systemctl - Control the systemd system and service manager
Example: `systemctl start service_name` (Start a system service)
29. journalctl - Query the systemd journal
Example: `journalctl -u service_name` (View the logs of a specific service)
30. scp - Securely copy files between hosts
Example: `scp file.txt user@host:/path/to/destination` (Copy a file to a remote host)
31. grep -r - Search for text recursively in files and directories
Example: `grep -r "pattern" directory/` (Search for a pattern recursively in a directory)
32. sed - Stream editor for filtering and transforming text
Example: `sed 's/foo/bar/' file.txt` (Replace occurrences of "foo" with "bar" in a file)
33. awk - Text processing and pattern scanning language
Example: `awk '{ print $1 }' file.txt` (Print the first column of a file)
34. ssh-keygen - Generate SSH key pairs
Example: `ssh-keygen -t rsa` (Generate an RSA SSH key pair)
35. systemctl status - Display the status of a systemd unit
Example: `systemctl status service_name` (Check the status of a service)
36. diff - Compare files line by line
Example: `diff file1.txt file2.txt` (Compare two files and show the differences)
37. head - Output the first part of files
Example: `head -n 10 file.txt` (Display the first 10 lines of a file)
38. tail - Output the last part of files
Example: `tail -n 5 file.txt` (Display the last 5 lines of a file)
39. tar -xvf - Extract files from a tar archive
Example: `tar -xvf archive.tar` (Extract files from a tar archive)
40. history - Display the command history
Example: `history` (Show a list of previously executed commands)
41. ln - Create links between files
Example: `ln -s file.txt link.txt` (Create a symbolic link to a file)
42. mount - Mount a file system
Example: `mount /dev/sda1 /mnt` (Mount a partition to a mount point)
43. umount - Unmount a file system
Example: `umount /mnt` (Unmount a mounted file system)
44. chmod +x - Make a file executable
Example: `chmod +x script.sh` (Make a script executable)
45. grep -v - Invert match and exclude lines matching a pattern
Example: `grep -v "pattern" file.txt` (Print lines not containing the pattern)
46. kill - Terminate a process
Example: `kill process_id` (Terminate a process by its ID)
47. systemctl enable - Enable a systemd unit to start on boot
Example: `systemctl enable service_name` (Enable a service to start automatically)
48. chown -R - Change ownership recursively
Example: `chown -R user:group directory/` (Change the ownership of a directory and its contents)
49. useradd - Create a user account
Example: `useradd username` (Create a new user account)
50. usermod - Modify user account properties
Example: `usermod -aG groupname username` (Add a user to a group)
51. passwd - Change user password
Example: `passwd username` (Change the password for a user)
52. systemctl restart - Restart a systemd unit
Example: `systemctl restart service_name` (Restart a service)
53. sort - Sort lines of text files
Example: `sort file.txt` (Sort the lines of a file alphabetically)
54. which - Locate the executable of a command
Example: `which command` (Find the location of a command's executable)
55. crontab - Schedule periodic tasks
Example: `crontab -e` (Edit the user's crontab file)
56. ssh-key-copy - Copy SSH public key to a remote server
Example: `ssh-copy-id user@host` (Copy SSH public key to a remote server)
57. ln -s - Create a symbolic link
Example: `ln -s /path/to/file link_name` (Create a symbolic link to a file)
58. history -c - Clear command history
Example: `history -c` (Clear the command history)
59. alias - Create an alias for a command
Example: `alias l='ls -l'` (Create an alias "l" for the "ls -l" command)
60. echo - Print a message
Example: `echo "Hello, World!"` (Print the message "Hello, World!")
61. systemctl stop - Stop a systemd unit
Example: `systemctl stop service_name` (Stop a service)
62. gzip - Compress files
Example: `gzip file.txt` (Compress a file using gzip)
63. gunzip - Decompress files compressed with gzip
Example: `gunzip file.txt.gz` (Decompress a file compressed with gzip)
64. tar -cvf - Create a tar archive
Example: `tar -cvf archive.tar directory/` (Create a tar archive of a directory)
65. tar -tvf - View the contents of a tar archive
Example: `tar -tvf archive.tar` (List the files in a tar archive)
66. df -h - Display disk space usage in a human-readable format
Example: `df -h` (Show disk space usage in a human-readable format)
67. df -i - Display inode usage
Example: `df -i` (Display inode usage)
68. ifconfig -a - Display all network interfaces
Example: `ifconfig -a` (Display all network interfaces)
69. netstat -tuln - Display listening ports
Example: `netstat -tuln` (Show listening ports)
70. systemctl reload - Reload a systemd unit configuration
Example: `systemctl reload service_name` (Reload a service configuration)
71. systemctl disable - Disable a systemd unit from starting on boot
Example: `systemctl disable service_name` (Disable a service from starting automatically)
72. free -m - Display memory usage in megabytes
Example: `free -m` (Show memory usage in megabytes)
73. ps -ef - Display a snapshot of the current processes
Example: `ps -ef` (Display all running processes)
74. ssh-keygen -p - Change passphrase of an SSH private key
Example: `ssh-keygen -p` (Change the passphrase of an SSH private key)
75. history -w - Write the current history to the history file
Example: `history -w` (Write the current history to the history file)
76. find -type f -name - Search for files with a specific name
Example: `find /path/to/directory -type f -name "filename"` (Search for a file by name)
77. locate - Find files by name
Example: `locate file.txt` (Find the path of a file by name)
78. systemctl list-units - List all systemd units
Example: `systemctl list-units` (List all active systemd units)
79. cat file1.txt file2.txt - Concatenate multiple files and display the content
Example: `cat file1.txt file2.txt` (Concatenate the content of two files)
80. grep -i - Perform a case-insensitive pattern search
Example: `grep -i "pattern" file.txt` (Search for a pattern case-insensitively)
81. chmod -R - Change permissions recursively
Example: `chmod -R 755 directory/` (Change the permissions of a directory and its contents recursively)
82. wc -l - Count the number of lines in a file
Example: `wc -l file.txt` (Count the number of lines in a file)
83. tail -f - Output the last part of a file and follow its changes
Example: `tail -f file.txt` (Display the last part of a file and follow new lines as they are appended)
84. chgrp - Change group ownership
Example: `chgrp groupname file.txt` (Change the group ownership of a file)
85. gzip -d - Decompress files compressed with gzip
Example: `gzip -d file.txt.gz` (Decompress a file compressed with gzip)
86. tar -xvf - Extract files from a tar archive
Example: `tar -xvf archive.tar` (Extract files from a tar archive)
87. awk '{print $NF}' - Print the last field of each line
Example: `awk '{print $NF}' file.txt` (Print the last field of each line in a file)
88. sort -r - Sort lines of text files in reverse order
Example: `sort -r file.txt` (Sort the lines of a file in reverse order)
89. sed 's/foo/bar/g' - Replace all occurrences of a string with another string
Example: `sed 's/foo/bar/g' file.txt` (Replace all occurrences of "foo" with "bar" in a file)
90. tail -n +2 - Display all lines of a file except the first line
Example: `tail -n +2 file.txt` (Display all lines of a file except the first line)
91. tee - Read from standard input and write to standard output and files
Example: `command | tee file.txt` (Execute a command and write its output to a file)
92. df -h -T - Display disk space usage with file system type
Example: `df -h -T` (Show disk space usage with file system type)
93. ps aux | grep process_name - Display information about a specific process
Example: `ps aux | grep sshd` (Display information about the SSH daemon process)
94. mount -t - Mount a specific file system type
Example: `mount -t ext4 /dev/sda1 /mnt` (Mount an ext4 file system to a mount point)
95. df -h - Display disk space usage in a human-readable format
Example: `df -h` (Show disk space usage in a human-readable format)
96. tar -xvf - Extract files from a tar archive
Example: `tar -xvf archive.tar` (Extract files from a tar archive)
97. tar -tvf - View the contents of a tar archive
Example: `tar -tvf archive.tar` (List the files in a tar archive)
98. df -h - Display disk space usage in a human-readable format
Example: `df -h` (Show disk space usage in a human-readable format)
99. df -i - Display inode usage
Example: `df -i` (Display inode usage)
100. ifconfig -a - Display all network interfaces
Example: `ifconfig -a` (Display all network interfaces)
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!