Overview
- An In-Memory data structure store
- Can be used for caching
- Supports strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets and other data structures.
Prerequisites
- Operating System: Ubuntu 18
- Command Line Interface or Terminal
Installation via Tarball
Installing via tarball is recommended as it is compiled from source.
01. Open a terminal window
From our partners:
02. Install build-essential, which will be used for building redis from source
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install -y build-essential
Install also tcl.
$ sudo apt-get install -y tcl
03. Download the stable version of redis
$ wget http://download.redis.io/redis-stable.tar.gz
04. Unpack and build redis
$ tar xvzf redis-stable.tar.gz $ cd redis-stable $ sudo make
Wait until the make command finish, this might take some time.
Then run <strong>make install</strong>
$ sudo make install
05. As hinted by redis, it is a good idea to run the make test command.
$ sudo make test
This will also take some time.
06. Create the directories.
$ sudo mkdir /etc/redis $ sudo mkdir /var/lib/redis $ sudo mkdir /var/log/redis
07. Copy the template configuration file you’ll find in the root directory of the Redis distribution into /etc/redis/
$ sudo cp redis.conf /etc/redis/redis.conf
08. Edit the redis configuration file and apply the following.
| daemonize | yes |
| pidfile | /var/run/redis-server.pid |
| logfile | /var/log/redis/redis-server.log |
| dir | /var/lib/redis |
$ sudo nano /etc/redis/redis.conf
Update the following
... # By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it. # Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized. daemonize yes ... # If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup # and removes it at exit. # # When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is # specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid file # is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid". # # Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it # nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally. pidfile /var/run/redis-server.pid ... # Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force # Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard # output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null logfile /var/log/redis/redis-server.log ... # The working directory. # # The DB will be written inside this directory, with the filename specified # above using the 'dbfilename' configuration directive. # # The Append Only File will also be created inside this directory. # # Note that you must specify a directory here, not a file name. dir /var/lib/redis
09. Copy the init script that you’ll find in the Redis distribution under the utils directory into /etc/init.d
$ sudo cp utils/redis_init_script /etc/init.d/redis-server
10. Edit the init script and apply the following.
If you changed the port in /etc/redis/redis.conf to a port other than 6379. Update the init script by setting the REDISPORT value to the same port you have set in redis configuration.
$ sudo nano /etc/init.d/redis-server
Update the config as follows. This setup is for running a single instance of redis, and adding a custom restart command, which just calls the stop and start as a convenience method.
#!/bin/sh
#
# Simple Redis init.d script conceived to work on Linux systems
# as it does use of the /proc filesystem.
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: redis-server
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Redis data structure server
# Description: Redis data structure server. See https://redis.io
### END INIT INFO
REDISPORT=6379
EXEC=/usr/local/bin/redis-server
CLIEXEC=/usr/local/bin/redis-cli
PIDFILE=/var/run/redis-server.pid
CONF="/etc/redis/redis.conf"
case "$1" in
start)
if [ -f $PIDFILE ]
then
echo "$PIDFILE exists, process is already running or crashed"
else
echo "Starting Redis server..."
$EXEC $CONF
fi
;;
stop)
if [ ! -f $PIDFILE ]
then
echo "$PIDFILE does not exist, process is not running"
else
PID=$(cat $PIDFILE)
echo "Stopping ..."
$CLIEXEC -p $REDISPORT shutdown
while [ -x /proc/${PID} ]
do
echo "Waiting for Redis to shutdown ..."
sleep 1
done
echo "Redis stopped"
fi
;;
status)
PID=$(cat $PIDFILE)
if [ ! -x /proc/${PID} ]
then
echo 'Redis is not running'
else
echo "Redis is running ($PID)"
fi
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
*)
echo "Please use start or stop as first argument"
;;
esac
11. Add the new Redis init script to all the default runlevels.
$ sudo update-rc.d redis-server defaults
12. Configure redis server to start on system boot
$ sudo update-rc.d redis-server enable
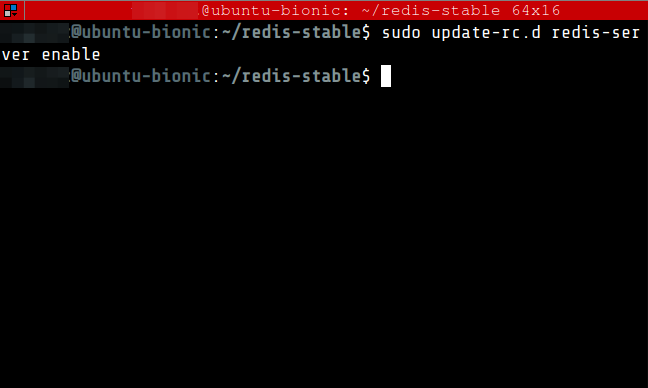
13. Restart the server redis-server
$ sudo service redis-server restart
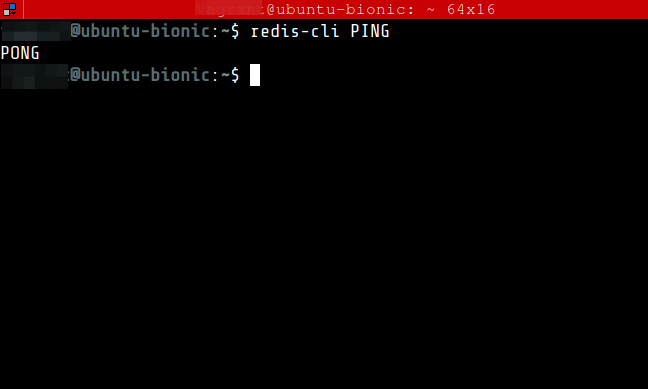
14. Test Redis by running the following command. It should return a PONG.
$ redis-cli PING
15. Exit from the redis-cli
$ exit
16. Test Redis functionality by performing simple operations. Access the redis CLI
$ redis-cli
17. Add new key-value pairs. An OK message should be returned.
127.0.0.1:6379> set pi 3.14159
18. Retrieve the value.
127.0.0.1:6379> get pi
Installation by Package Manager
If via Package Manager, the version of Redis may be outdated.
01. In the command line
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install -y redis-server
02. Test Redis by running the following command. It should return a PONG.
$ redis-cli PING
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!