At enterprises across industries, documents are at the center of core business processes. Documents store a treasure trove of valuable information whether it’s a company’s invoices, HR documents, tax forms and much more. However, the unstructured nature of documents make them difficult to work with as a data source. We call this “dark data” or unstructured data that businesses collect, process and store but do not utilize for purposes such as analytics, monetization, etc. These documents in pdf or image formats, often trigger complex processes that have historically relied on fragmented technology and manual steps. With compute solutions on Google Cloud and Document AI, you can create seamless integrations and easy to use applications for your users. Document AI is a platform and a family of solutions that help businesses to transform documents into structured data backed by machine learning. In this blog post we’ll walk you through how to use Serverless technology to process documents with Cloud Functions, and with workflows of business processes orchestrating microservices, API calls, and functions, thanks to Workflows.
At Cloud Next 2021, we presented how to build easy AI-powered applications with Google Cloud. We introduced a sample application for handling incoming expense reports, analyzing expense receipts with Procurement Document AI, a DocAI solution for automating procurement data capture from forms including invoices, utility statements and more. Then organizing the logic of a report approval process with Workflows, and used Cloud Functions as glue to invoke the workflow, and do analysis of the parsed document.
From our partners:
We also open sourced the code on this Github repository, if you’re interested in learning more about this application.
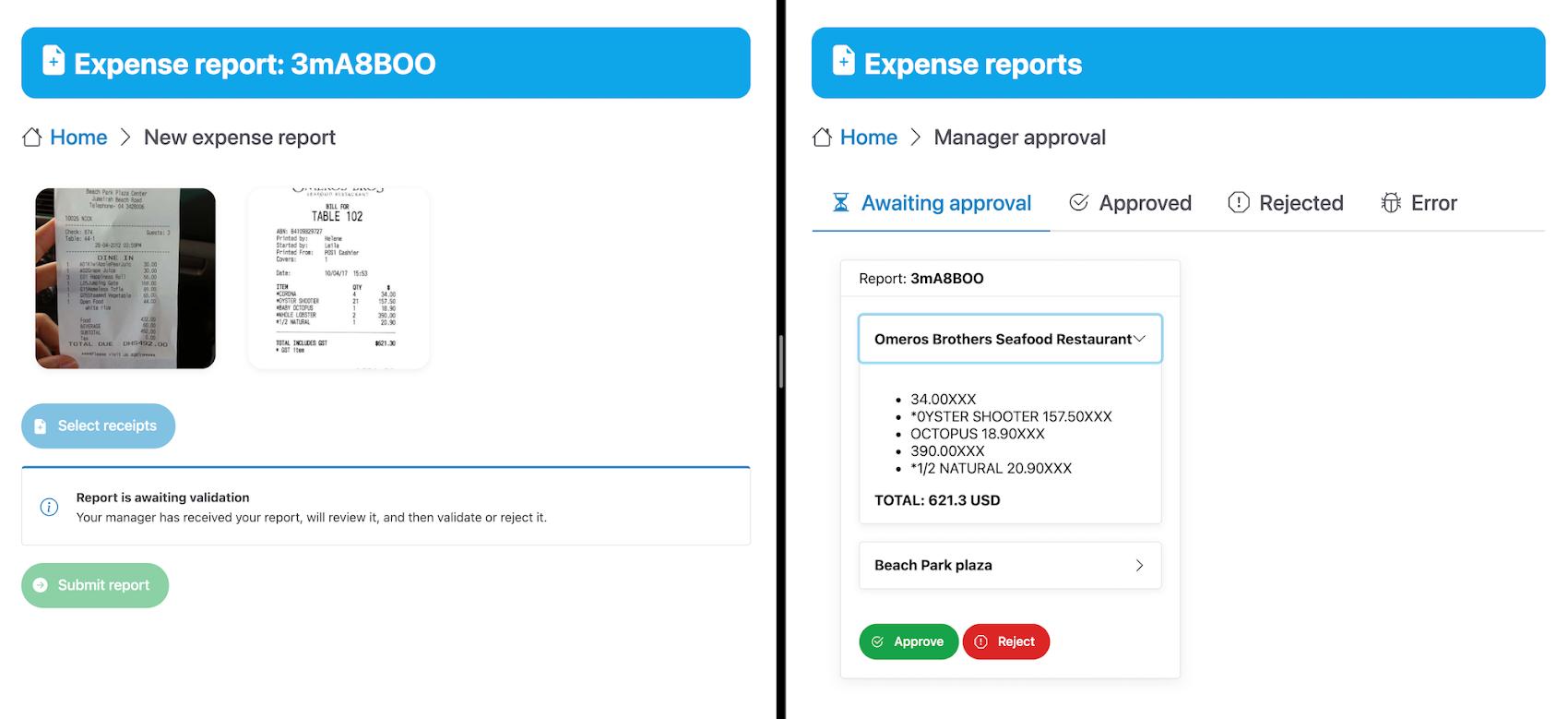
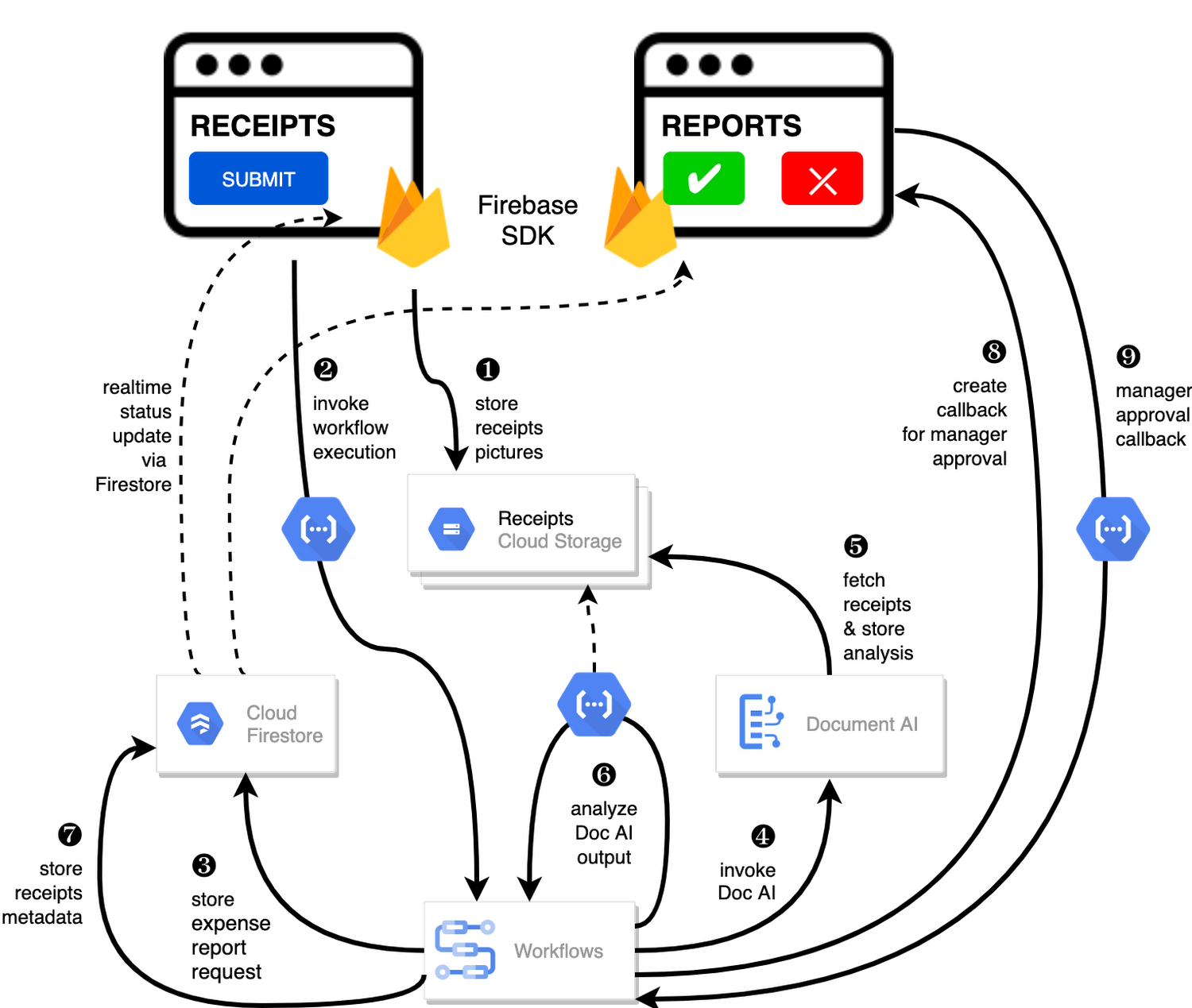
In the above diagram, there are two user journeys: the employee submitting an expense report where multiple receipts are processed at once, and the manager validating or rejecting the expense report.
First, the employee goes to the website, powered by Vue.js for the frontend progressive JavaScript framework and Shoelace for the library of web components. The website is hosted via Firebase Hosting. The frontend invokes an HTTP function that triggers the execution of our business workflow, defined using the Workflows YAML syntax.
Workflows is able to handle long-running operations without any additional code required, in our case we are asynchronously processing a set receipt files. Here, the Document AI connector directly calls the batch processing endpoint for service. This API returns a long-running operation: if you poll the API, the operation state will be “RUNNING” until it has reached a “SUCCEEDED” or “FAILED” state. You would have to wait for its completion. However, Workflows’ connectors handle such long-running operations, without you having to poll the API multiple times till the state changes. Here’s how we call the batch processing operation of the Document AI connector:
- invoke_document_ai:call: googleapis.documentai.v1.projects.locations.processors.batchProcessargs:name: ${"projects/" + project + "/locations/eu/processors/" + processorId}location: "eu"body:inputDocuments:gcsPrefix:gcsUriPrefix: ${bucket_input + report_id}documentOutputConfig:gcsOutputConfig:gcsUri: ${bucket_output + report_id}skipHumanReview: trueresult: document_ai_response
Machine learning uses state of the art Vision and Natural Language Processing models to intelligently extract schematized data from documents with Document AI. As a developer, you don’t have to figure out how to fine tune or reframe the receipt pictures, or how to find the relevant field and information in the receipt. It’s Document AI’s job to help you here: it will return a JSON document whose fields are: line_item, currency, supplier_name, total_amount, etc. Document AI is capable of understanding standardized papers and forms, including invoices, lending documents, pay slips, driver licenses, and more.
A cloud function retrieves all the relevant fields of the receipts, and makes its own tallies, before submitting the expense report for approval to the manager. Another useful feature of Workflows is put to good use: Callbacks, that we introduced last year. In the workflow definition we create a callback endpoint, and the workflow execution will wait for the callback to be called to continue its flow, thanks to those two instructions:
- create_callback:call: events.create_callback_endpointargs:http_callback_method: "POST"result: callback_details...- await_callback:try:call: events.await_callbackargs:callback: ${callback_details}timeout: 3600result: callback_requestexcept:as: esteps:- update_status_to_error:...
In this example application, we combined the intelligent capabilities of Document AI to transform complex image documents into usable structured data, with Cloud Functions for data transformation, process triggering, and callback handling logic, and Workflows enabled us to orchestrate the underlying business process and its service call logic.
Going further
If you’re looking to make sense of your documents, turning dark data into structured information, be sure to check out what Document AI offers. You can also get your hands on a codelab to get started quickly, in which you’ll get a chance at processing handwritten forms. If you want to explore Workflows, quickstarts are available to guide you through your first steps, and likewise, another codelab explores the basics of Workflows. As mentioned earlier, for a concrete example, the source code of our smart expense application is available on Github. Don’t hesitate to reach out to us at @glaforge and @asrivas_dev to discuss smart scalable apps with us.
By: Guillaume Laforge (Developer Advocate) and Anu Srivastava (Senior Developer Relations Engineer, Google Cloud)
Source: Google Cloud Blog
For enquiries, product placements, sponsorships, and collaborations, connect with us at [email protected]. We'd love to hear from you!
Our humans need coffee too! Your support is highly appreciated, thank you!